Table of Contents
The Unified soil classification system was first introduced by Casagrande and was adopted for the first time by the Corps of Engineers of the United States of America in 1942.
✔ A unified classification of soils is the most commonly adopted classification system of soil for engineering purposes.
It is, in fact, the universally accepted soil classification system.
✔ In this classification system, the soil is classified based on both the plasticity characteristics and the particle size of the soil.

✔ Each group is identified using a group symbol. The group symbol consists of primary and secondary descriptive letters.
| Primary Letters | Secondary Letters |
| G: Gravel | W: Well Graded |
| S: Sand | P: Poorly Graded |
| M: Silt | M: Non-Plastic Fines |
| C: Clay | C: Plastic Fines |
| O: Organic | L: Low Plasticity |
| Pt: Peat | H: High Plasticity |
This system classifies the soil into 15 different groups. The major divisions, however, include three categories namely coarse-grained soils, fine-grained soils, and highly organic soils.
Major Divisions of Unified Soil Classification System (USCS)
The major divisions of the soil according to this classification have been briefly described as follows:
a. Coarse-Grained Soil
✔ According to the Unified system of soil classification, the soil is coarse-grained if more than 50% of the soil is retained on a 0.075mm sieve.
Coarse-grained soil is further categorized into gravel (G) and sand (S).
✔ The coarse-grained soil is gravel if more than 50% of the coarse particles are retained on the 4.75mm sieve else it is sand.

b. Fine-Grained Soil
✔ According to the Unified system of soil classification, the soil is fine-grained if more than 50% of the soil passes through a 0.075mm sieve.
Fine-grained soil is further categorized into Low plastic (L) and High plastic (H).
This subdivision of the fine-grained is done based on the plasticity characteristics of the soil.
✔ In case the liquid limit of the soil is less than 50, it is grouped in the soil with a low plasticity group whereas if the liquid limit of the soil is more than 50, it is grouped in the soil with a high plasticity group.
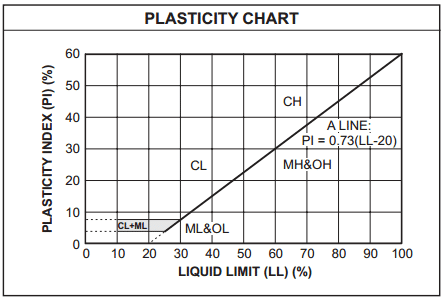
The Unified soil classification system has provided a plasticity chart based on the data on the liquid limit and the plasticity index.
A line on the chart is known as the A-line. If the data on the LL and PL plot both lies above the A-line then the soil is classified as clay.
✔ If the data lies below the A-line then the soil is classified as either inorganic silt or organic silt which are further distinguished by oven drying. If the drying of the silt reduces the LL by 30% or even more, the soil is organic else the soil is inorganic silt.

c. Highly Organic Soil
✔ Organic soils are simply fine-grained soils essentially consisting of organic characteristics.
Some of such organic characteristics include high compressibility, dark color, strong odor, prominent visible organic materials, etc.
✔ The organic soils are further classified as organic soil of low plasticity (symbolized as OL), organic soil of high plasticity (symbolized as OH), and Peat (symbolized as Pt).
| Read More: Classification of Soils |
| Read More: Prismatic Compass |