Table of Contents
In this article, we will discuss the silt content test.
1. Introduction
Silt content is a fine material that is below 150 microns. Silt content is unstable in the presence of water.
The maximum amount of silt not only decreases the bonding of cement and fine aggregates but also heavily affects the strength and durability of the mortar.
2. Silt Content Test
2.1. Objective
To find out silt content in the sand (fine aggregate).
2.2. Apparatus Required
a. 250 ml measuring cylinder
b. Water
c. Sand and Tray
2.3. Test Procedure
a. First, we have to fill the measuring cylinder with a 1% mixture of salt and water up to 50 ml.
b. Add sand to it until the level holds out 100 ml. Then fill the fluid up to 150 ml level.
c. Envelope the cylinder and vibrate it well. After 3 hours, the silt will be settled down over the sand layer.
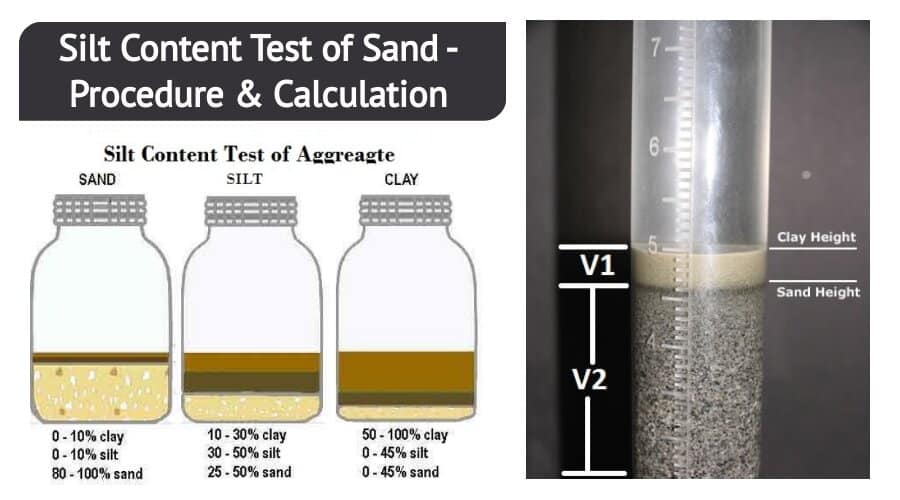
d. Now list down the silt layer alone volume as V1 ml (settled over the sand).
e. Then list down the sand volume below the silt as V2 ml.
f. Repeat the procedure two more times to get the average.
Silt Content = (V1 / V2) x 100%
For example, for a given sand sample, if V1 is 9 and V2 is 130, the % silt content would be 6.9 %.

2.4. Result
The permissible value of silt content in Sand is 8%.
2.5. Observation Table
| Description | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 |
| The volume of sample Sand (V2) | |||
| The volume of the silt layer (V1) | |||
| Percentage of silt | |||
| Average |
2.6. Advantages
a. It helps us to determine the pure quantity of sand present in the sand sample and also helps in the separation of high or low silt-containing sand (high silt containing sand is unsuitable for constructional use and vice versa).
| Read More: Types of sand |
| Read More: Properties of Aggregates |