Table of Contents
| Summary: When there is an immediate requirement for the road at a low budget, the need is fulfilled by constructing the low-cost road. Low cost roads are constructed utilizing local labor and materials and can be easily upgraded to blacktopped or concrete roads when traffic increases. Earth roads, kankar roads, gravel roads & WBM roads are some low cost roads. |
1. What is a low cost road?
The road constructed and maintained at a low cost by utilizing locally available materials & labor is a low cost road.
“You must focus on short road alignment, minimal use of heavy machines, using local materials and manpower as far as possible. “
✔ It is also referred to as a cheap road.
✔ The main aim of low-cost roads involves optimizing design, materials, and methods to deduct expenses while maintaining safety and functionality.
✔ In the villages and underdeveloped areas, the immediate need for roads can be fulfilled at a low cost by these roads and can be improved further if required.
✔ Low-cost roads are primarily constructed in Hilly and Himalayan regions where building roads is extremely challenging due to unstable slopes, high erosion, unsupportive climate, and high transportation costs, which ultimately lead to high material and labor costs.
✔ From the field visit in different rural parts of Nepal, we found that low cost road commonly focuses on the following:
~ Minimizing the number of earthworks
~ Minimizing complex and expensive activities
~ Using local and cheap materials
~ Utilizing local human resources
Features of Low Cost Road:
✔ Low construction cost
✔ Use of locally available materials & labor
2. How many types of low cost roads are there?
There are 4 types of commonly used low cost roads :
a. Earth Road
b. Kankar Road
c. WBM Road
d. Gravel Road
a. Earth Road

The type of low-cost road in which pavement structure is constructed with the soil available at the site is called earth road.
✔ It is also known as the earthen road.
✔ This road is most feasible in rocky areas. It is not suitable in rainy regions.
✔ In sloppy areas like Hilly and Himalayan, low cost roads like gravel or kankar roads were unsuitable due to the movement of materials from higher elevations to lower. So, we found that earth roads were mostly utilized.
How many types of earth roads are there?
Two types of earth roads are common in practice:
a. Ordinary Earth Road
b. Stabilized Earth Road
| Feature | Ordinary Earth Road | Stabilized Earth Road |
|---|---|---|
| Foundation and wearing surface | Natural soil | Stabilized soil |
| Maintenance | Frequent | Less frequent |
| Durability | Less durable | More durable |
| Load-bearing capacity | Lower | Higher |
| Traffic suitability | Light traffic | Heavy traffic |
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
| Suitability for weighty vehicles | Not suitable | Suitable |
| Dustiness | Dusty | Less dusty |
| Rut formation | Prone to ruts | Less prone to ruts |
i. Ordinary Earth Road
The type of earth road whose foundation and the wearing surface comprise one or two compacted layers of natural soil along its alignment is an ordinary earth road.
✔ It is the first stage of road construction.
Features:
a. It requires frequent maintenance. Mainly in the rainy season.
b. It is dusty, and ruts are formed quickly.
c. It is not suitable for the movement of weighty vehicles.
d. It is very economical to construct.
ii. Stabilized Earth Road
A road with a foundation and wearing surface comprising one or two compacted layers of stabilized soil is called a stabilized earth road.
✔ Stabilized earth roads can withstand high loads and traffic compared to ordinary.
This road is also more durable than ordinary earth roads.
Features:
a. It doesn’t require frequent maintenance like ordinary earth roads.
b. Initial construction cost is more as compared to the ordinary earth road.
[ Note:
Stabilized Soil: Soil stabilized with physical, chemical, or biological agents to increase strength and durability ]
b. Kankar Road

✔ Kankar Road is constructed utilizing kankar (or chips of impure limestone) as the chief material.
Kankar is mainly found in African countries, south asian countries, Australia, and many more regions.
✔ It is only constructed when limestones are available in sufficient quantity.
✔ Kankar road is constructed by spreading the kankar above the subgrade and compacting it with mechanical or manual means.
To improve the water-resistant capacity of the road, a thin layer of bitumen can be applied on the surface of the kankar road.
| Advantages of Kankar Road | Disadvantages of Kankar Road |
| Cheaper to construct | Dusty and ruts are formed quickly |
| Environment Friendly | Requirement of frequent maintenance ( mainly after the rainfall or monsoon ) |
| Easy to construct and maintain | Not suitable for high-speed or heavy traffic |
c. WBM Road
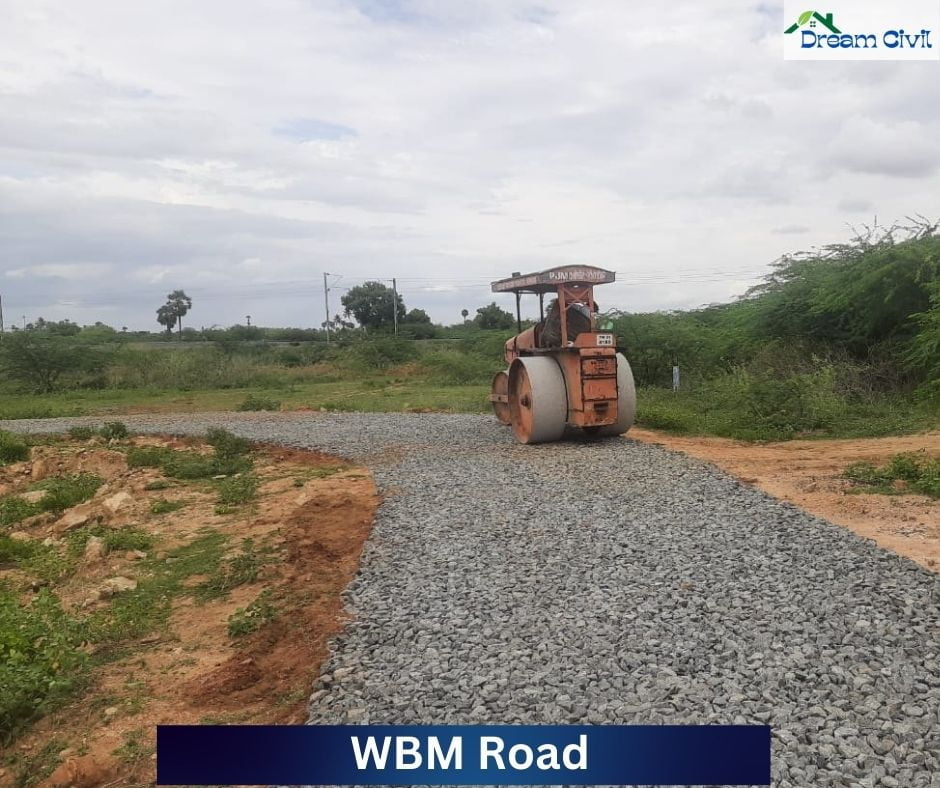

WBM road is the pavement whose surface course comprises crushed or broken aggregates mechanically interlocked by rolling. Voids are filled using filler materials with water assistance.
✔ WBM road produces dust while providing service.
✔ Powder of Calcium Chloride or Bituminous Materials can be spread on the road’s surface to minimize dust.
✔ This road is not suitable for fast-moving vehicles.
✔ In many villages and rural areas, WBM road is constructed initially and further improved or paved when the fund is available.
[ Note:
What does WBM stand for?
WBM stands for Water Bound Macadam. ]
d. Gravel Road

✔ Gravel road is surfaced with gravel brought to the site from a quarry or stream bed.
✔ This road is commonly constructed by spreading a thin layer of gravel above the subgrade and compacted using rollers.
3. How low cost road constructed?
The construction of low cost roads includes the following steps:
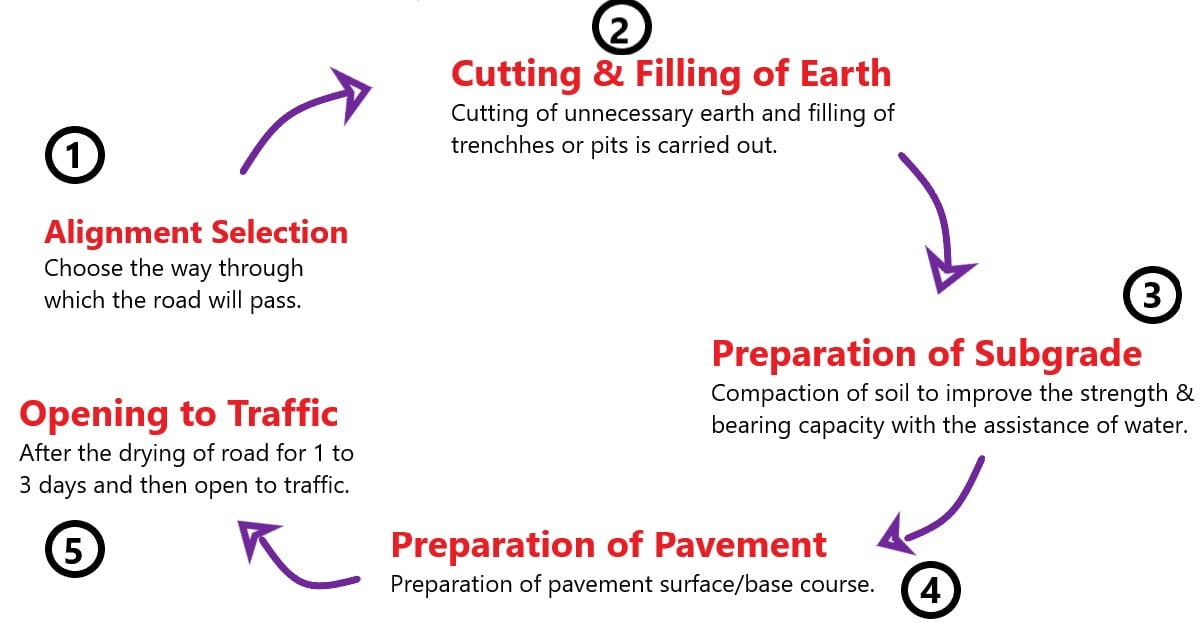
a. Alignment Selection

✔ The alignment shows the path through which the road will pass. So, the selection of road alignment should be made such that it has less conflict, high soil strength & shorter length.
✔ Road alignment is the key factor influencing construction speed and economy.
| Read the Article: Road Alignment with Principles, factors controlling, types, and more. |
b. Cutting and Filling of Earth

✔ Cutting and filling work of earth is carried out to provide proper shape to the road.
✔ During this process, retaining wooden logs (or bamboo) walls are provided if the side slope is unstabilized. In the absence of wooden logs, locally available stones are used.
c. Preparation of Sub-grade

✔ Sub-grade preparation involves soil compaction to increase strength, stability, and bearing capacity.
✔ Compaction of subgrade should be done with the assistance of water.
✔ Road strength is determined by subgrade. So, the subgrade should be compacted multiple times (according to the soil type).
d. Preparation of Pavement Layer

✔ Above the subgrade, a material layer (pavement layer) is provided. This layer works as the base as well as the surface course.
✔ No additional layer is required above the subgrade to construct an earth road, as the subgrade acts as the pavement layer.
| Road Type | Pavement Material |
| Kankar Road | Kankar |
| WBM Road | Crushed Aggregate |
| Gravel Road | Gravel |
✔ The pavement layer is compacted, similar to the subgrade, with water assistance.
e. Drying
✔ The road is allowed to dry naturally for 1 to 3 days and then opened to traffic.
4. What are the considerations for low cost roads?
The considerations that need to be taken care of in low-cost roads are:
1. Following the mass curve, The road shall be constructed on a balanced approach.
2. The road shall be constructed in stages.
3. Local materials shall be used.
4. Local workforce should be utilized.
5. Planning shall be done in a decentralized manner.
6. Bio-engineering shall be practiced for slope stability (instead of a costlier structure).
7. The cross slope of the road shall be towards the outside to avoid the side drain.
8. In the case of natural water resources, a causeway shall be preferred instead of bridges, culverts, or other costlier construction.
9. The garbage and wooden log walls shall be preferred instead of the retaining walls.
5. What are the pros of the low cost road?
Some of the pros of the low-cost road are:
1. No significant investment of capital is required.
2. Local people and materials are utilized.
3. As bio-engineering is preferred for slope protection. It is more environmentally friendly.
4. Stage construction technique helps manage disputes at the construction site.
5. The cost of side drain construction can be saved.
6. It helps to mobilize rural materials.
7. It can be upgraded to the blacktopped road when required.
6. What are the cons of the low cost road?
Some cons of the low-cost road are:
a. Not suitable for heavy traffic.
b. The requirement of maintenance after heavy rainfall.
c. Low comfort & high vehicle operation cost.
7. FAQs
| Question | Answer |
| 1. Why is low cost road cheap? | Local labor and materials are utilized to construct this road. This reduces construction costs. |
| 2. Is this road used in developed countries? | Yes, in rural areas of developed countries, this road is used. |
| 3. How much does this road cost to build? | 20 to 25% of the budget for Flexible Pavement or 10 to 15% of the budget of Rigid Pavement. |
| 4. Are there only 4 types of low-cost roads? | No, there is no relevant detail regarding how many low-cost roads there are. We have written only 4 common types of low cost roads in this article. |
| 5. Can low cost roads be upgraded? | Yes, You can easily upgrade. |
| Read Also: Types of Pavement Failure |
| Verified Article By Civil Engineer Madhu Krishna Poudel |

