Table of Contents
In this, we will discuss the floor space index.
1. Introduction
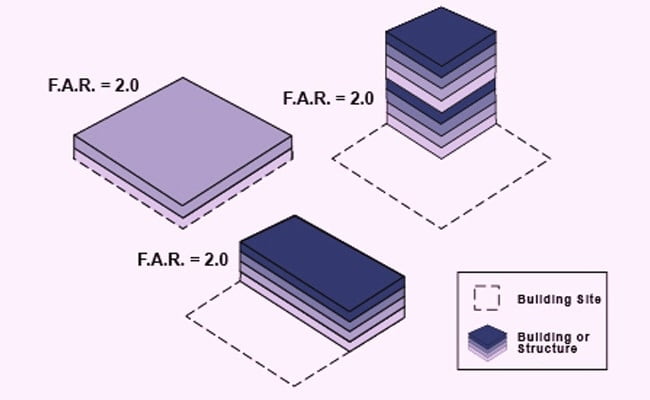
FSI full form is the Floor space index, also known as FAR whose full form is the Floor area ratio. It may be defined as the building’s area covered by all floors to the plot area given.
The maximum area that can be given to construct a plot and maximum height up to which construction can be done on a plot.
It can be different from state to state, it depends upon the rules and regulations provided by that particular municipality.

The different points that are seen while defining the value of FSI for a site are as follows.
a. Type of Occupancy ( Residential or Non-residential)
b. Type of Construction
c. Front street Width of the proposed building and traffic load.
d. The locality and density of the area where the building is proposed
e. Parking amenities
f. Drainage, water supply, and fire fighting abilities.
2. Importance of FSI
It helps to choose the developer construction limit on a plot of land. FSI mainly handles the building vertical development and living situations in metro cities.
If any municipality gives permission for a higher FSI, which leads to more dense construction.
Similarly, If any municipality gives permission for a lesser FSI, which leads to less dense construction.
| Read Also: Building plan |
3. Formula to Calculate FSI
The formula to calculate the FSI is the Total covered area of all floors divided by plot area.
FSI = Total covered area of all floors / Plot area.
National Building Code has provided the specific value of FSI for different occupancies and types of construction.
if the area of a plot is 600 Sqm and the FSI specified by the municipality for the site is 1.2, then the maximum area of the building that can be built on that plot will be =1.2 × 600 = 720 Sqm.
Depending on the road width in front of the plot, we can build four-storeyed buildings, with each floor area of 187.5 Sqm, or a three-storeyed building with each floor area of 250 Sqm.
The formula to calculate the built-up area is,
Allowable Built-Up Area = Plot Area X FSI
Allowed number of Floors = (Total Built-Up Area)/ (Maximum Plot Coverage)
Example:
Total plot area- 30,000 m2
Maximum FSI= 4
Total Built-up area= 30,000×4 = 120,000 m2
Maximum plot coverage= 40%
40% of 30,000 = 12,000 m2
so,
Maximum Plot Coverage in Ground Floor = 12000 Sqm
Maximum Numbers of Floors = Total Built-Up Area/Maximum Plot Coverage
120,000/12000= 10
Maximum number of floors is 10.
| Read Also: Building Information Modeling |
4. Advantages of FAR
1. It helps handle the open area to built area ratio.
2. FSI directs the city skyline.
3. An average Floor Space Index value satisfies a sound development.
4. With Floor Space Index, we can hold a move toward balanced, sustained, and planned growth.
5. Disadvantages of FAR
It is taken as FSI is a bad indicator of physical form. Lesser value of FSI impacts accommodation and employment chances for the population. With the mean value of the Floor Space Index, it may be changed into an asset and shape the end product to resolve all the issues.