Table of Contents
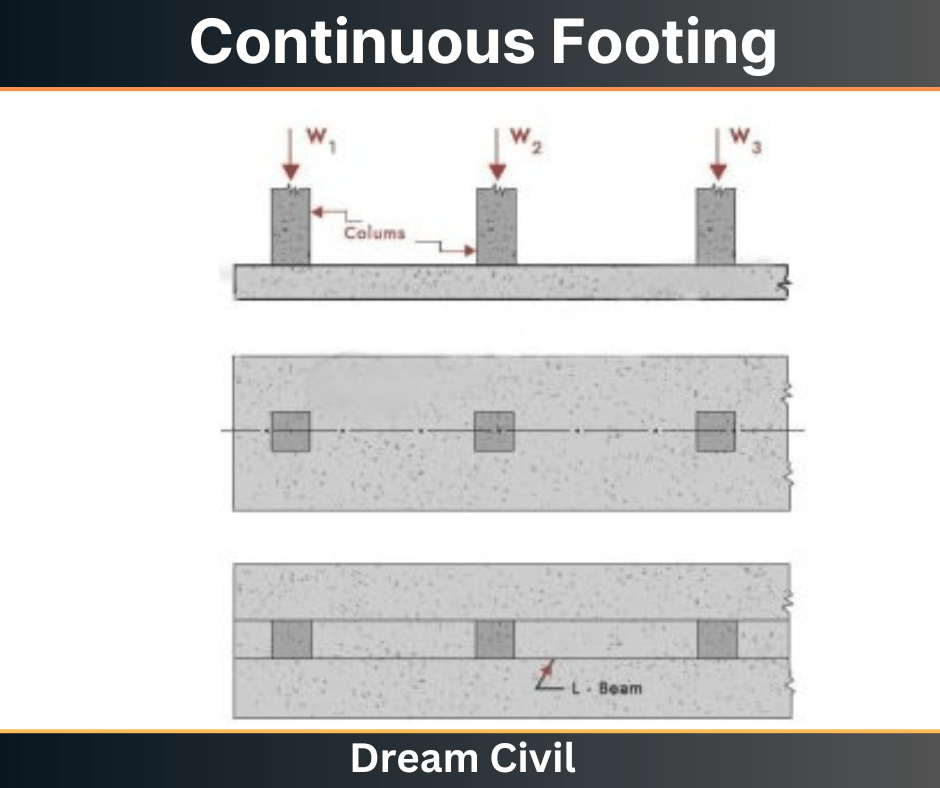
The type of shallow foundation that supports more than two columns in a row/line is called continuous footing.
The shape of this footing is commonly rectangular but sometimes trapezoidal too.
It is generally used if the columns in a row are closer.
This footing is analogous to the strip footing for the wall.
The loads from the individual columns are transferred either directly to the footing slab, or through a longitudinal beam running longitudinally when the loads are heavy.
1. Types of Continuous Footing
a. Simple Continuous Footing
No steps are provided in this type of continuous footing.
It is cheaper to construct as compared to the stepped continuous footing.
b. Stepped Continuous Footing
The footing having two or more steps is stepped continuous footing.
It is costlier and more complex to construct as compared to the simple continuous footing.
This footing is able to withstand more loads as compared to simple.
The figure below shows how steps are formed in the stepped continuous footing.

2. Uses
The continuous footing is used when;
i. The load-bearing capacity of soil is low.
ii. The columns are too close to each other and their individual footing will overlap.
3. Advantages
a. Provides a stable base and transfers the load to a larger area.
b. Evenly supports the weight of the foundation walls.
4. Disadvantages
a. Not suitable for horizontally unstable grounds.
b. Needs a large amount of earthwork.
5. References1. Content Filter & Authenticity Checking Team, Dream Civil International (Our team checks every content & detail to maintain quality.) |
Read More: Overhanging Beams

