Table of Contents
In common practice, the bill of quantities is referred to as the BOQ or BQ.
A Bill of quantities may be defined as the document that is prepared in the construction industry to specify the various materials, labors, and resources along with their costs.
The bill of quantities is a means of communication tool between three main parties of any construction project i.e. the Client, the Consultant, and the Contractor.
Precisely, a bill of quantities may be defined as the document of schedule which categorizes, describes, and quantifies the materials and other items that are necessary for the construction work.
The bill of quantities also enlists or details the various terms and conditions as well as the description of various items of work identified by the specifications and the drawings in the tender document to enable the Contractor to price the works during the tendering process.
It is often prepared by the Quantity Surveyor or the Cost Consultant.
BOQ is necessary throughout the project mainly during both the pre-contract and the post-contract phases.
It is a general practice to prepare the bill of quantities in a tabular form.
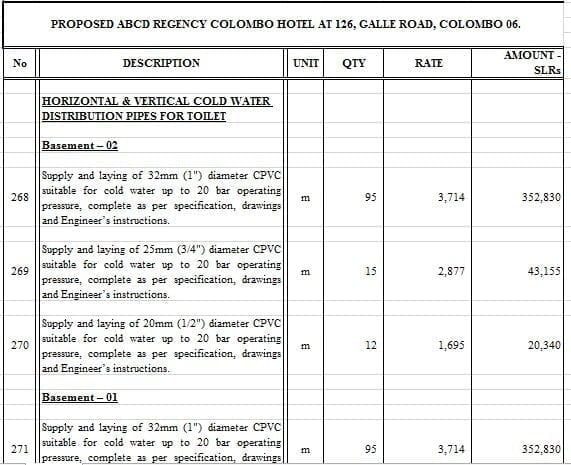
Figure: A sample of BOQ
2. Importance of Bill of Quantities
The main importance of preparing the bill of quantities can be listed as follows:
1. It is necessary to determine the total estimated contract price.
2. It gives a rough idea about the entire project.
3. It provides the quantities to the contractors concerning which the contractors can bid.
4. It determines the extent of the work to be performed.
5. It provides the schedule of rates and is important for preparing the variation orders and assists in the valuation.
6. It serves as the basis for the valuation of the interim payments.
7. It is also important for the preparation of the final bill amount.
3. Major Parts of Bill of Quantities
The parts of the bill of quantities may vary from place to place depending upon the size of the project, prevailing practices, etc.
In general, the bill of quantities consists of three major parts namely the preliminaries, the measured works, and the provisional sum which has been further described below:
a. Preliminaries
In the construction industry, the preliminaries refer to the indirect costs that are incurred during the execution of the project and are inevitable for the completion of the project.
These indirect costs are grouped in a separate category as it is difficult to distribute them among the measured works.
Some of the examples of the preliminaries can be duly listed as follows:
a. Cost for maintenance of the site.
b. Charges for the performance bond and advance payment guarantee.
c. Compensation charges such as workmen compensations.
d. Costs for ensuring site safety.
e. Charges of the project management professionals.
f. Costs for the drawings.
b. Measured Works
Measured works enlist the items of work that are inevitable for the completion of the project.
These works can be measured in different units such as meter, square meter, cubic meter, number, etc.
The value of such measured work is obtained by multiplying the quantity and the prevailing rate of each item of the work.
c. Provisional Sums
Provisional sum refers to the price that is included for the various items of work that need to be carried out during the execution of the project but the price of those works cannot be quoted or fixed at the tendering phase.
It is usually adjusted during the execution phase of the project.
4. Standards for Preparing of Bill of Quantities
Since the bill of quantities serves as a communication medium between the parties involved in a construction project, a standard that is widely accepted must be used for its preparation.
When the bills of quantities are prepared by standards, misunderstandings or ambiguities and disputes among the parties may be avoided.
Some of the common standards that are used for the preparation of the bill of quantities can be listed as follows:
1. Standard Method of Measurement, UK (Previously used).
2. New Rules of Measurement, UK (Replaced Standard Method of Measurement on 1st July 2013).
3. Civil Engineering Method of Measurement (the standard method for work measurement).
4. Common Arrangement of Work Sections (the standard method for work categorization).
5. Preparation of Bill of Quantities
When preparing the bills of quantities, a series of steps must be carried out in proper order to make the bill of quantities managed and easy to understand.
In the preparation of the bill of quantities, the first step includes taking off the quantities from the working drawings.
The taken-off measurements from the working order must be in a particular order which can easily be recognized.
Such measurement recording sheet is known as TDS(Technical Data Sheet).
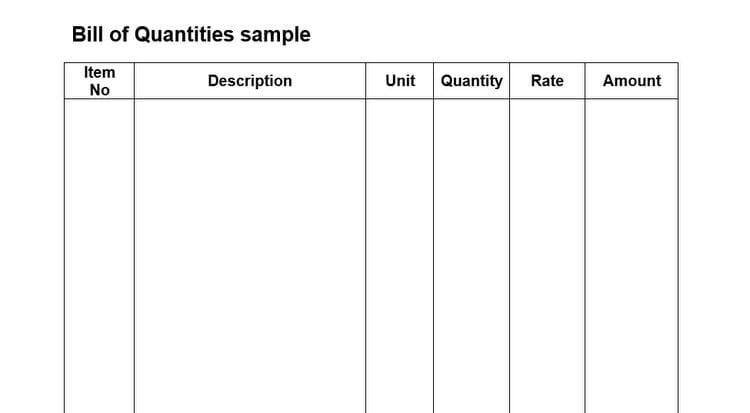
Figure: Framework of the BOQ Sheet
As shown in the figure above, then the units and the quantities of the measured work are filled.
Then, the standard rates for the particular item of work are filled.
Finally, the amount is determined by multiplying the quantity and the rate for each item of work.
6. Common Mistakes in Bill of Quantities
Some of the common mistakes that may occur during the preparation of the bill of quantities can be listed as follows:
1. Incorrect measurement of the quantities of various items of work.
2. Inclusion of unnecessary or irrelevant preliminaries.
3. Omissions of the items of work.
4. Discrepancies in the items of work and the drawings and specifications.
5. Double counting and double listing of items of work.
6. Lack of consideration of the differences in the currencies.
7. Inaccurate assumptions regarding the various items of work.
8. Arithmetic Errors.
7. Advantages of Bill Of Quantities
The advantages of the Bill of quantities are as follows:
1. It assists to calculate the interim variations and payments.
2. It assists in the overall project management as it delivers the data required for different aspects of project management such as monthly progress reports, life cycle cost, etc.
3. It assists in future estimating and cost planning.
4. It delivers a clear picture of the works that must be done.
8. Disadvantages of Bill Of Quantities
The disadvantages of the Bill of quantities are as follows:
1. It may be incorrect in case the estimator is uneducated.
2. It must be performed carefully else enormous arithmetic errors may succeed.
9. FAQ
1 How to calculate Steel?
⇒ 1. The weight of the bar in kg/m should be determined as (d2 ÷ 162)
where,
‘d’ is the diameter of the bar in mm.
2. ‘L‘ for column main steel in footing should be evaluated as a minimum of 30cm per as specified.
3. For bent bar keep 0.42d in a straight length of the bar
where,
’ d is the clear depth of beam/slab.
2. What is the Bill of Quantities?
⇒ A Bill of Quantities (BOQ or BQ) is documentation established to define the quality and amount of work needed to be done by the main contractor to finish a project. It is designed by a quantity surveyor or cost consultant.
3. What is the purpose of the Bill of Quantity?
⇒Various purposes of the Bill of Quantity are detailed below:
1. It is useful in cost planning before tendering process.
2. Tendering-useful in passing significant construction tenders.
3. It gives a basic idea to investors about the cost of the project.
4. It gives a basis for the valuation of variation.
4. What is the meaning of BOQ in the tender?
⇒ BOQ stands for Bill of Quantities in Tendering. Bill of Quantity provides an opinion about the cost of a project that is tendering firm willing to deliver. This detail is essential for them to serve a higher or lower rate concerning their rate while contracting.
| Read More: Construction Waste |
