Table of Contents
The art of construction of stone units bonded together with mortar is called stone masonry. The stone masonry constructed using finely dressed stone blocks is called ashlar masonry.
✔ The stone blocks used may be either square or rectangular.
✔ The height of stone varies from 25 to 30 cm.
Some features of ashlar masonry are:
a. The courses are of uniform height.
b. All the joints of this masonry are regular, thin, and have a uniform thickness.
c. Ashlar masonry is mostly used in the construction of heavy structures, architectural buildings, high piers, and abutments of bridges.
✔ The height of blocks in each is kept equal but it is not necessary to keep all the courses of the same height.
Types of Ashlar Masonry
Ashlar masonry may be divided into the following categories:

a. Ashlar Fine Tooled Masonry
This is the finest type of stone masonry work.
Each stone is cut to the regular and required size and shape to have all sides rectangular so that the stone gives perfectly horizontal and vertical joints with adjoining stones.
The beds, joints, and faces are chisel-dressed, such that all waviness and unevenness are completely removed and a fairly smooth surface is obtained.
The face which remains exposed in the final work is so dressed that no point on the dressed face is more than 1 mm from a 600 mm long straight edge placed on the surface in any direction.
The top and bed are also so dressed that no point on the surface is more than 3 mm, from the straight edge.
The side surfaces to form the vertical joints are also depressed that no point on the surface is more than 6 mm from the straight edge.
The surfaces forming internal joints which are not visible are also so dressed that at no point in the surface is more than 10 mm from the straight edge.
All the angles and edges that remain exposed in the final position are kept as true square and free from chipplings. The thickness of courses is generally less than 15 cm. The width of the stone is not kept less than its height.
Headers and stretchers are laid alternatively in each course or courses of headers and courses of stretchers may be laid alternatively or they may be laid as otherwise directed.
The thickness of the mortar joint is finely pointed.

b. Ashlar Rough Tooled Masonry (Bastard Ashlar)
In this type of masonry, the beds and sides of each stone block are finely chisels dressed just in the same manner as for ashlar fine, but the exposed face is dressed by rough tooling.
A strip, about 25 mm wide and made utilizing a chisel is provided around the perimeter of the roughly dressed faces of each stone.
The rough tooled face when tested with a straight edge 600 mm in length, should not show any point on the surface to vary by more than3 mm in any direction.
This type of masonry is also known as bastard masonry.
The size, angles, edges, etc are maintained in order, similar to that for fine-dressed ashlar.
The thickness of the mortar joint should not be more than 6 mm.

| Read Also: Quarrying of stone |
c. Ashlar Rock or Quarry Faced
In this type of masonry, the exp[osed surface face of the stone is not dressed but is kept as such to give rock facing. However, a strip of about 25 mm wide, made utilizing a chisel, is provided around the perimeter of the exposed face of every stone.
The projections on the exposed face (Known as bushings) exceeding 80 mm in height are removed by light hammering. Each stone block, however, is maintained true to its size, with perfectly straight side faces and beds, and truly rectangular.
This type of construction gives a massive appearance. The height of each block may vary from 15 cm to 30 cm. The thickness of the mortar joint may be up to 10 mm.

d. Ashlar Chamfered Masonry
This is a special form of rock-faced ashlar masonry in which the strip provided around the perimeter of the exposed face is chamfered or beveled at an angle of 45º employing a chisel to a depth of 25 mm.
Due to this, a groove is formed in between adjacent blocks of stone.
Around this beveled strip, another strip of 15 cm is dressed with the help of a chisel. The space inside this strip is kept rock-faced except that large bushings over 80 mm projections are removed by a hammer.

e. Ashlar Block in Course Masonry
This type of masonry is intermediate between rubble masonry and ashlar masonry.
The faces of each stone are hammer-dressed, and the height of blocks is kept the same in any course though it is not necessary to keep the uniform height for all the courses.
The vertical joints are not as straight and as fine as in ashlar masonry.
The depth of courses may vary from 15 to 30 cm.
This type of masonry is adopted in heavy works such as:
✔ Retaining walls
✔ Bridges

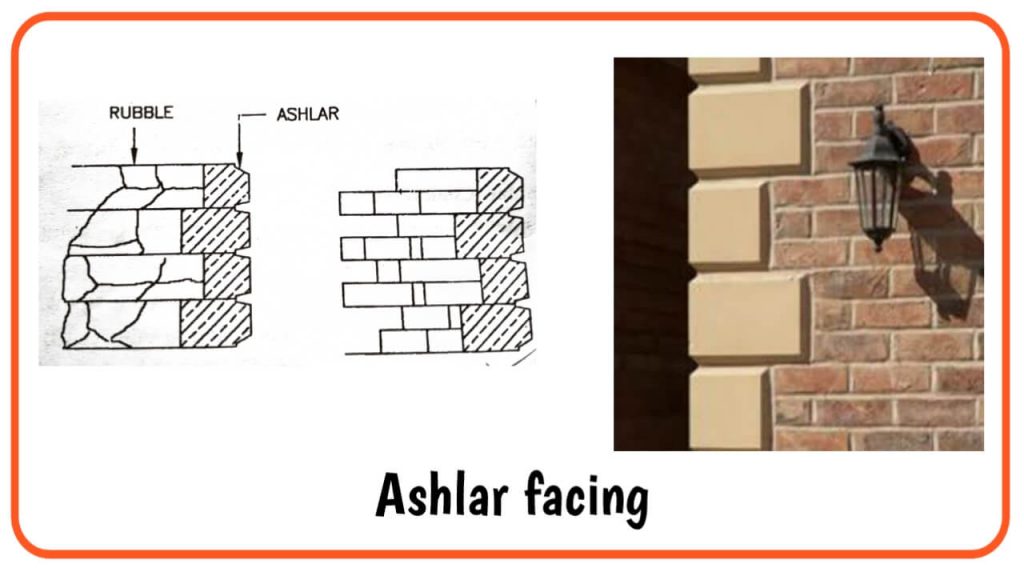
f. Ashlar Facing
Ashlar facing masonry is provided along with brick or concrete block masonry, to give a better appearance.
The sides and beds of each block are properly dressed to make them true to shape.
The exposed faces of the stones are tough tooled and chamfered. The backing of the wall may be made in brick masonry.
| Read Also: Artificial Stones |

