Table of Contents
Screening of water is the first process in water treatment that is done to remove suspended or floating solid particles like branches, leaves, sticks, etc from the water.
When water derived from the surface contain large suspended as well as floating matters which may be sticks, branches, leaves, etc; the screens are fixed in the intake works or at the entrance of the treatment plant to remove the suspended as well as floating matters.

Fig: Screening of Water
Screening can be done manually using screens or by the use of screening machines.
Chain-driven screens, continuous belt screens, catenary screens, and reciprocating rakes are the commonly used screening machines.
| Read Also: Irrigation with its all types |
1. Purpose of Screening of Water
The purposes of screening of water are as follows:
1. To remove large suspended as well as floating matter such as leaves, branches, dead animals, etc.
2. To work as a protective device for successive treatment. (It prevents the clogging of pumps and damage to other equipment.)
3. To increase the efficiency of the successive.
2. Types of Screens Used in Screening of Water
Commonly, two types of screens are used for screening which are listed below:
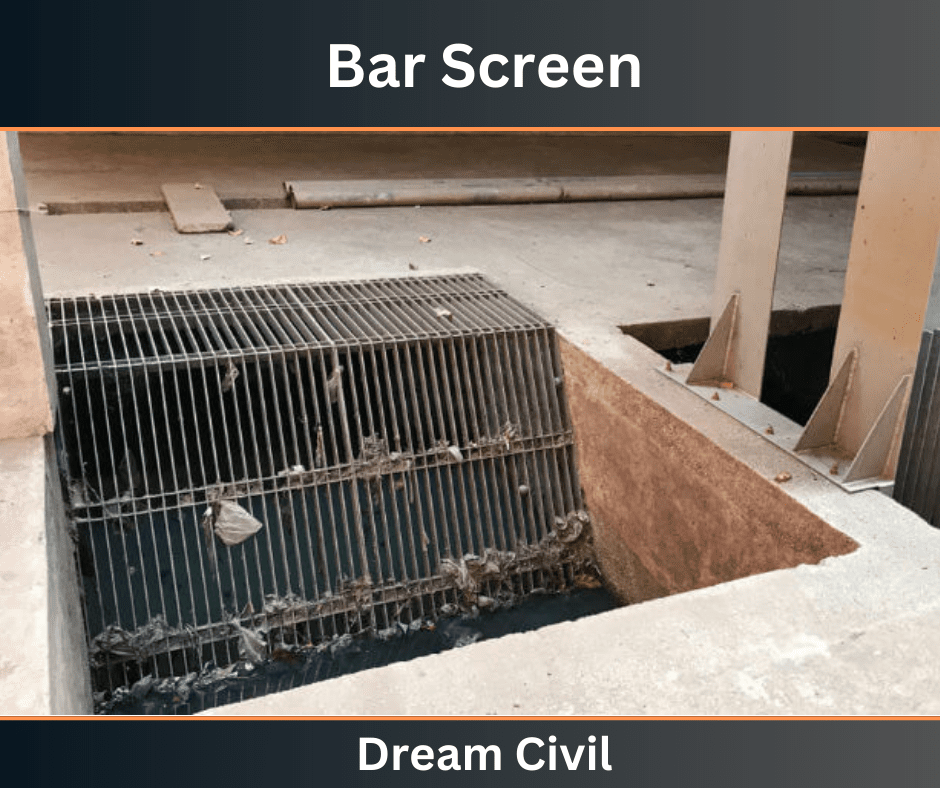
a. Bar Screen
The bar screen is also called the coarse screen.
They have a wider opening and are placed in front of the fine screen to remove large, floating, and suspended materials.
The coarse screen has openings ranging from 6 to 150 mm (0.25 to 6 in).
b. Fine Screen
The fine screen is used to remove smaller, floating, and suspending matter of size smaller than removed by the coarse screen.
The fine screen has openings of less than 6 mm.

c. Micro Screen
It is the smallest type of screen whose opening ranges from 10 to 35 µm.
These screens are typically low-speed drum screens.

Read Also: Water Treatment Processes

