Table of Contents
What is Road Pattern?
When the road is constructed in patterns like rectangular, radial, hexagonal, etc., it is called a Road Pattern. Road Pattern helps to properly manage traffic and interconnect the branch roads with the main roads.

The main principle of road patterns is to reduce the time and distance the vehicle takes to reach the destination. It also focuses on the interconnection of branch roads.
It increases the response time of average and emergency vehicles, like ambulances, fire engines, etc., to reach the destination.
Road Pattern also plays a vital role in traffic management, but most countries neglect it. 6 types of road patterns are primarily used.
2. What are the types of Road Patterns?
1. Rectangular or Block Pattern
a. In this pattern, the whole area is divided into rectangular blocks.
b. Streets or branch roads intersect with each other at the right angle.
c. The main roads always pass through the center and should be wide enough.
d. Branch roads may be narrow as compared to main roads.
e. The main roads should be provided with a direct approach outside the city.

Pros
~ The rectangular blocks can be further fractioned into small rectangles that may be used to construct buildings placed back to back, with roads on their front.
~ It is widely adopted on city roads.
~ Construction and Maintenance is quite easy.
Cons
~ It is not convenient because roads are perpendicular to each other. This increases the rate of accidents due to poor visibility at a perpendicular junction.
2. Radial or Star and Block Pattern
a. It combines star and block patterns.
b. The entire area is divided into a radial network of roads radiating outward from the center with a block pattern network of roads between the radial main streets.

Pros
~ Less risky as compared to the rectangular pattern.
~ It reduces the level of congestion at the primary bottleneck location.
~ If one radial road is blocked, another can be used as an alternative.
Cons
~ Lack of safety appurtenances like rail transitions, crash attenuators, and post-support bases.
~ It is only effective when two-lane ramp traffic does not have to merge at the downstream end of the ramp.
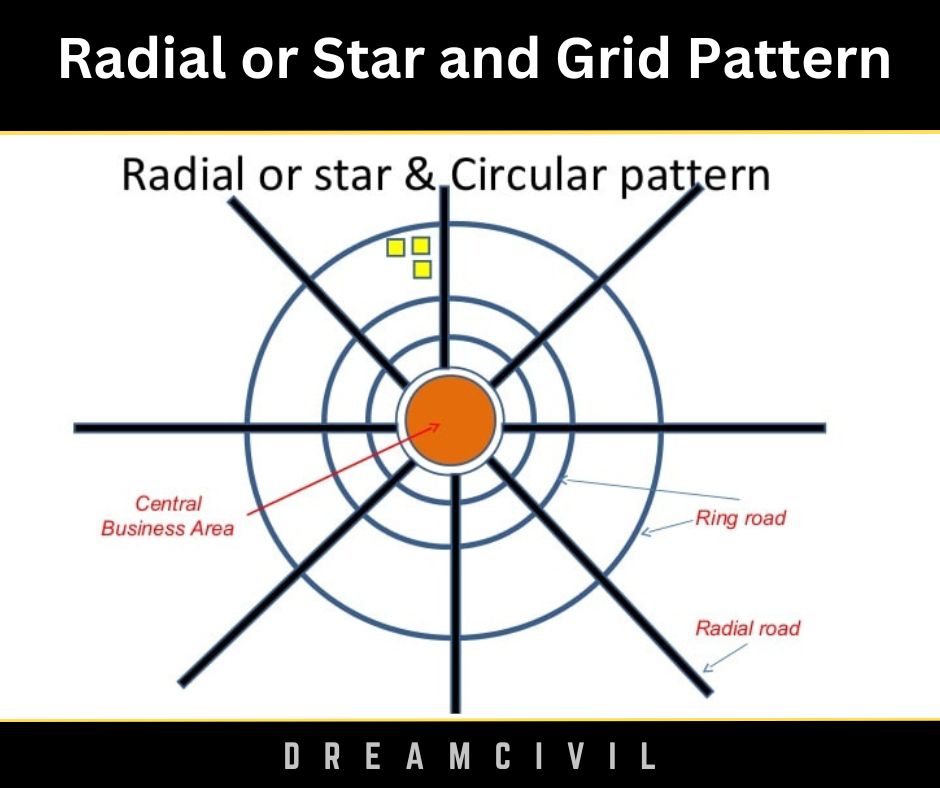
3. Radial or Star and Circular Pattern
a. It is the pattern in which the main roads(radial roads) radiate from the central point and are connected with concentric roads(ring roads) radiating outwardly.

Pros
~ It is safe as compared to the above patterns because vehicles travel in the same direction.
~ Roundabouts present in this pattern improve the efficiency of traffic flow. This also reduces fuel consumption and emissions of the vehicle.
~ Using a circular pattern in place of traffic signals reduces the possibility of rear-end crashes.
Cons
~ Providing a good curve while implementing this pattern is quite challenging.
~ It affects the driving ability. Mainly, old drivers face this problem due to declines(decreases) in vision, hearing, and cognitive functions.
~ There is the necessary, proper provision of the traffic signal, road markings, and lighting to alert the drivers that they are approaching a roundabout.
~ Splitter Islands should be extended far enough to provide pedestrian refuge (crosswalk) and to delineate(describe ) the roundabout.
4. Radial or Star and Grid Pattern
a. This pattern is formed by combining Star and Grid Pattern.
b. As in others, a radial road network radiates outwardly from the center. Then, the main radial streets are interconnected by providing a grid pattern.
Pros
~ It increases the efficiency of land usage and unit density.
~ It improves the traffic flow in both directions by utilizing Savannah’s cellular structure.
~ It provides high safety to vehicular traffic with a high proportion of 3-way intersections.
~ It reduces the cut-through traffic.
Cons
~ Splitter islands should be extended far enough.
~ High construction cost because of the need for extra traffic signals, road marking and lighting.
5. Hexagonal Pattern
a. In this, the entire area is divided into hexagonal patterns.
b. Three roads meet the built-up area boundary by the sides of the hexagons at every corner of the hexagon, which can be further divided into suitable sizes.

6. Minimum Travel Pattern
The city center is connected with suburban and neighboring centers with the shortest roads. To make the road short, the road alignment is made straight.
Read More: Prismatic Compass

