Table of Contents
1. Introduction
✔ An excavator is a heavy-duty machine consisting of a boom, dipper, Bucket, and cab on rotating platforms widely used for excavating soil, handling materials, or demolishing small structures. It can be used in plain as well as hilly regions.
✔ Excavators can also be used for loading materials in trucks, tractors, etc.
✔ The average weight of an excavator is 30,783 kg or(67,865 pounds) which is around 15+ times the weight of an average car.
We have provided the average weight of different types of excavators:
| Excavator Category | Weight Range |
| Mini Excavators | 0.5 to 9 tons |
| Small Excavators | 9 to 22.5 tons |
| Medium Excavators | 22.5 to 50 tons |
| Large Excavators | 50+ tons |
2. Uses of the Excavator
1. Earthmoving and Excavation:
a. Trenching:

✔ They are used for digging the trenches for pipelines, cables, and building foundations, ensuring everything’s laid down just right.
b. Site Preparation:

✔ When leveling land for construction or making way for beautiful landscapes, excavators swoop in like landscaper superheroes, efficiently clearing out unwanted soil and vegetation.
c. Grading and Sloping:

✔ Excavators shape the land with high precision, ensuring the right angles for drainage, roads, and whatever else is needed.
d. Material Handling:

✔ From loading trucks with materials to handling heavy materials like rocks, heavy pipes, etc, excavators are significant.
2. Construction and Demolition:
a. Foundation Digging:

✔ They are used for preparing the Site for the foundation construction of buildings, dams, bridges, and other structures.
b. Demolition:

✔ For the Demolition of the existing structures, excavators are significant.
c. Site Cleanup:

After the construction, it’s cleanup time! Excavators efficiently sweep in to clear debris and rubble, leaving the place completely neat and clean.
3. Mining and Quarrying:
a. Mineral and Ore Extraction:

✔ Excavators play a vital role in the mining industry, extracting valuable minerals and ores from the earth.
b. Overburden Removal:

✔ Before reaching the valuable stuff underground, excavators first remove the extra rocks and soil on top, and they call it overburden in the industry.
c. Loading and Hauling:

✔ Once extracted, excavators efficiently load minerals and ores onto trucks for transportation.
4. Landscaping and Agriculture:
a. Pond and Pool Creation:

✔ For that perfect pond or pool, excavators shape the terrain like artists at work. It’s like they’re sculpting a masterpiece in your backyard.
b. Land Development:

✔ Landscaping superheroes, that’s what they are! Excavators create terraces and pathways and mold hills and valleys according to your design dreams.
c. Tree Removal and Land Clearing:

✔ Clearing land for agricultural purposes or removing unwanted trees becomes effortless with the power and precision of an excavator.
5. Other Specialized Uses:
a. Forestry:

✔Certain excavator attachments allow for tree cutting, mulching, and clearing debris in forestry operations.
b. Disaster Relief:

✔ When disaster strikes, excavators are on the front lines. Clearing debris and creating emergency routes – they’re the unsung heroes in times of crisis.
c. Infrastructure Maintenance:

✔ Maintaining the lifelines of society! Excavators tackle everything from cleaning canals and waterways to patching up roads and bridges, ensuring our infrastructure stays strong.
3. Functional Parts of the Excavator
The main functional parts of the Excavator are;

a. Boom
b. Arm Cylinder
c. Bottom Roller
d. Bucket
e. Bucket Cylinder
f. Cab, ROPS
g. Car Body
h. Dipper, Arm, Stick, Crowd Cylinder
i. Track Pad, Grouser Pad
j. Final Drive, Reduction Assembly
k. H-Link
l. Main Control Valve
m. Counterweight
4. Types of Excavator
Different types of excavators are listed below:
a. Crawler Excavators
✔ The crawler excavator is also known as the “standard excavator” and can rotate 360 degrees for easy digging, moving, and dumping of materials.
✔ They have a boom and Bucket attached to the front of the machine. They use hydraulic power. They are slower than wheeled excavators.

✔ They run like tanks (i.e., two parallel rotating tracks).
✔ They are useful in mining, trench digging, landscaping, forestry, etc.
✔ They are good in steep, rough, or hilly landscapes.
Uses: They are used for preparing road alignments, mining, trench digging, landscaping, etc.
Pros: Suitable to use in plain as well as hilly areas.
Cons: Slower than other wheeled excavators.
b. Wheeled Excavator
✔ Wheeled excavators are similar to crawler excavators, but the only difference is that they are installed with wheels (tires) instead of tracks.

✔ They can rotate at 200 degrees.
✔ They save time and hauling costs because they provide excellent maneuverability and speed compared to crawler excavators.
Uses: Demolition work, digging, materials handling, etc.
Pros: Faster than crawler excavator, saves time and hauling cost.
Cons: Not suitable to use in muddy and hilly areas.
c. Suction Excavator
✔ A suction excavator is also known as a vacuum excavator.
✔ They loosen and remove soil precisely.
✔ The onboard air fans generate the suction power to draw up the material through the intake nozzle and deposit it in the container at 200 miles per hour.

✔ They are suitable when the area requires precise and careful excavating.
✔ They are not applicable for large-scale works because the intake nozzle ( suction pipe ) is 1 foot ( 30 centimeters ) or less in diameter.
✔ They are only suitable to excavate areas with loose soil surfaces.
Uses: Remove materials from the hole on land, heavy debris on land, etc.
Pros: Suitable when the area requires precise and careful excavating.
Cons: Not suitable for large-scale works.
d. Long Reach Excavator
✔ Long-reach excavators are similar to crawler excavators but feature longer extendable booms and arms.

✔ The length of the arm ranges from 40 – 100 feet.
✔ They can excavate in risky areas, such as safe places and hard-to-reach locations.
Uses: Digging deep holes or trenches
Pros: Suitable for demolition works that require precision and are helpful in hard-to-reach areas.
e. Hydraulic Shovel
✔ Hydraulic shovel excavators are also known as power shovels and are regarded as the most potent type of Excavator.

✔ They are equipped with a powerful engine and a large bucket.
Mainly useful for large-scale works.
Uses: Hauling rocks, soil, other heavy materials, and heavy digging projects.
Pros: Highly Powerful than other excavators.
f. Dragline Excavator
✔ Dragline excavators are giant Excavators that use a hoist rope system and dragline to raise & lower the Bucket.

Uses: Canal dredging, strip mining, deep pile driving, underwater operations, etc
g. Backhoe Excavator
✔ Backhoe excavators have an excavator boom on the machine’s backside, and the machine’s front part is installed with a large bucket or blade used for leveling moving soils and other materials.

✔ They can rotate at 200 degrees.
Uses: Landscaping, small demolitions, breaking asphalt, loading materials, etc.
Pros: Can perform multiple tasks.
h. Skid Steers
✔ Skid steers are smaller, making them suitable for work in narrow areas and limited workspace.
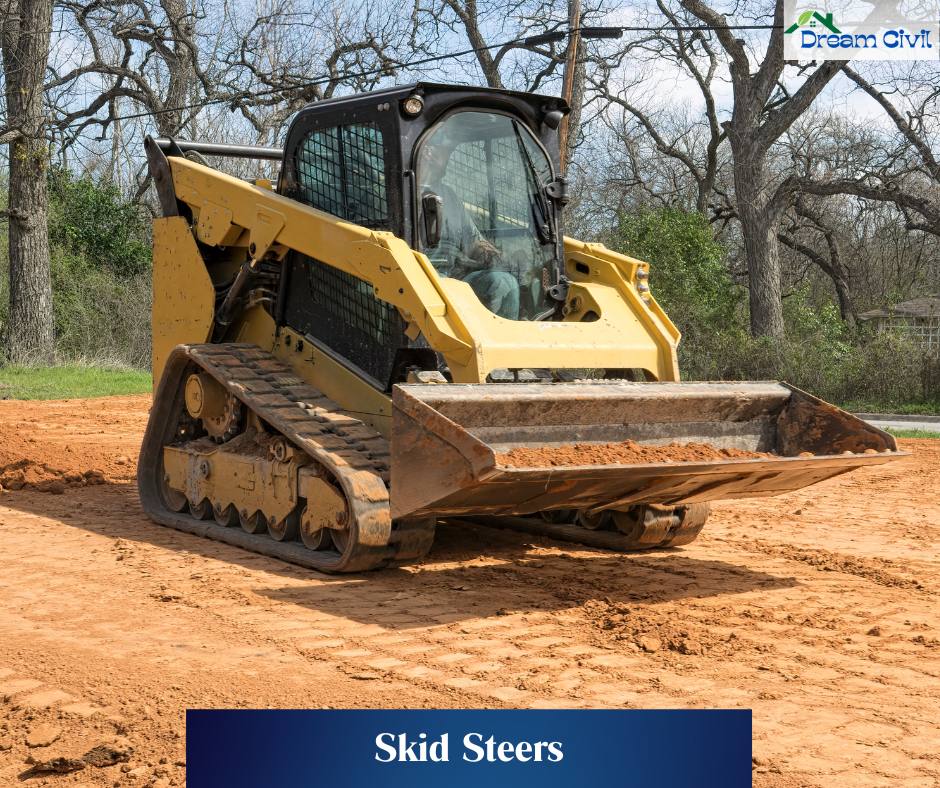

✔ The Bucket and Boom face away from the driver.
Uses: Clearing sites, removing debris, and pool cleaning.
i. Truck-Mounted Excavator
✔ Truck-mounted excavators are mounted on truck chassis and can run at higher road speeds.
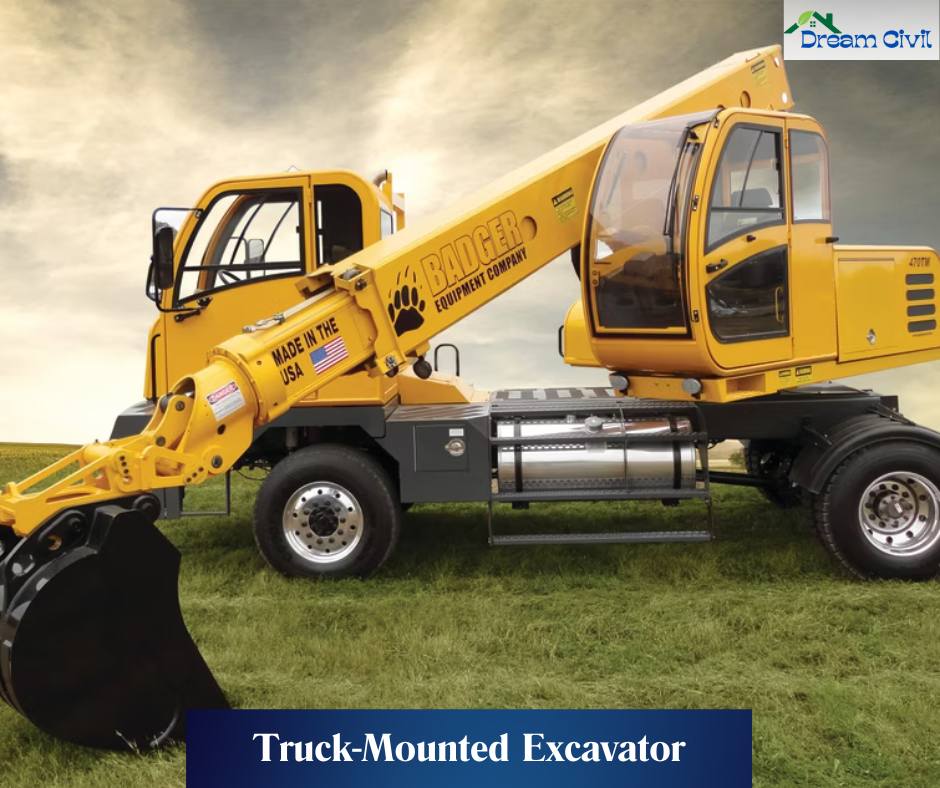

Cons: Require ample space and firm ground to function correctly.
j. Self-Propelled Excavator
✔ Self-propelled excavators are provided with rubble tires and small boom & buckets with a speed of 10-30 km per hour.
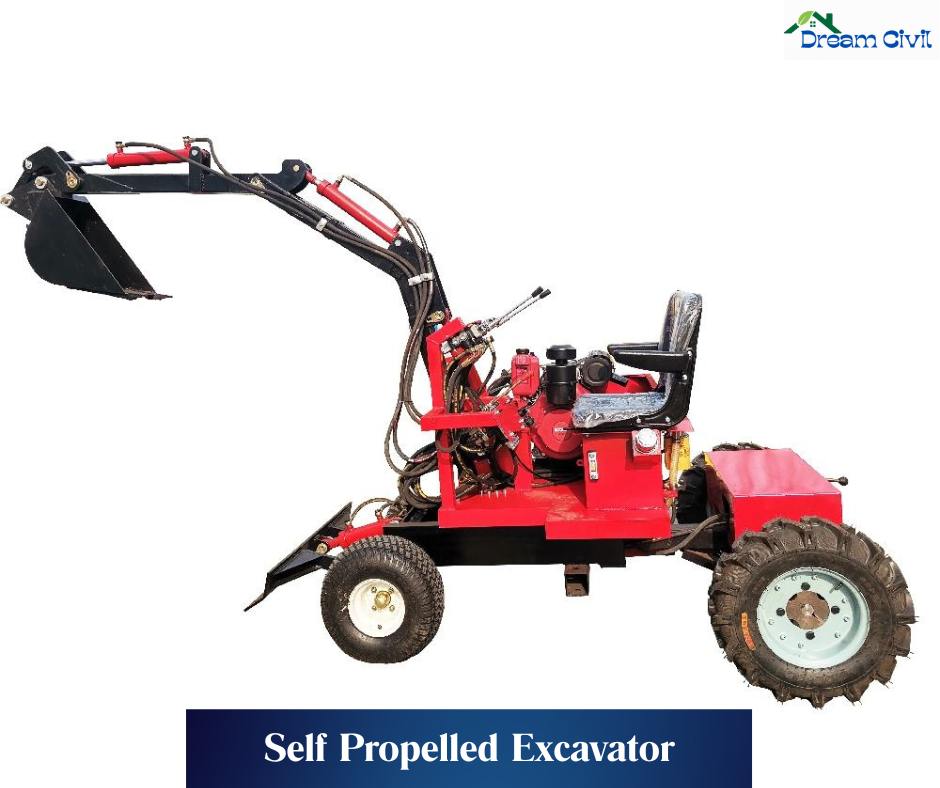

✔ They are provided with an engine and a cab.
Uses: Usually used for lifting small objects and excavating tiny areas ( like excavating small pits to plant trees ).
k. Excavator Mounted on a Barge/Rail
✔ The type of excavators used in railway lines or water are mounted on a barge.

l. Clamshell
✔ The type of excavators that have both the properties of cranes and a dragline are called clamshell excavators.
✔ They have a bucket of a shape similar to clam fish and have two shells hinged together.
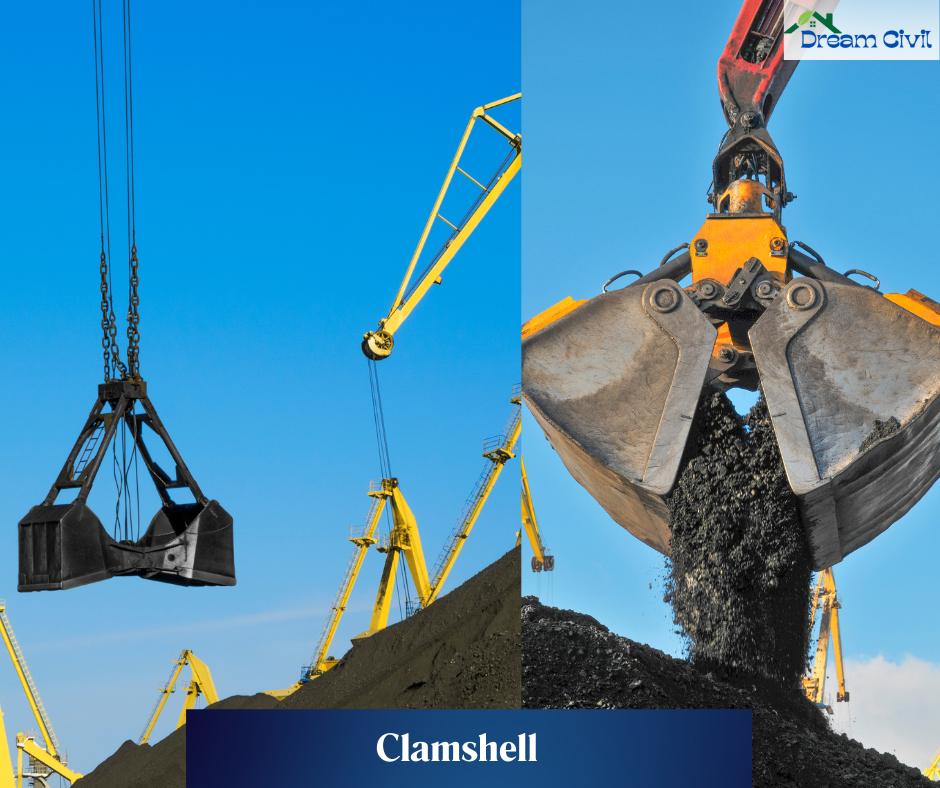

Uses: Carry/Handle loose and medium-hard materials.
Cons: Slow and less efficient.
m. Bucket-Wheel Excavator
(Note: The world’s largest and heaviest land vehicle is a Bucket-Wheel excavator named Bagger 293.)
✔ They are used for large-scale operations.
✔ They are installed with a digging wheel with buckets adjusted vertically on the boom.

Uses: Mining work, material handling, heap leaching, etc.
Pros: Useful for large-scale work
Cons: Most of their work is replaced by hydraulic excavators.
n. Dredger
✔ Dredger excavators are the type of excavators that are suitable when the work is carried out in lakes, rivers, and seas.

The types of dredgers are:
i. Dipper excavator
ii. Ladder excavator
iii. Suction excavator
Read Also: 27 Bathroom Accessories with Images
| Verified Article By Er. Madhu Krishna Poudel |

