Table of Contents
✔ Discover the world of Blockboard – an engineered wood product with softwood strips sandwiched between hardwood veneers. Learn about its technical properties, types, manufacturing processes, applications, etc.
✔ Find out how to choose the right Blockboard for your project and work with it effectively. Explore comparisons with plywood and MDF and understand its resistance to water and fire. Get all the insights you need about Blockboard in one place.
1. Summary table of Blockboard

| Summary | Blockboard |
|---|---|
| Definition | ✔ Blockboard is an engineered plywood made of softwood strips sandwiched between hardwood veneers. |
| Technical properties | ✔ Modulus of elasticity long, Density, bending Strength, bending strength cross, formaldehyde emission, Modulus of elasticity cross, fire safety category, thickness tolerance, length and width tolerance |
| Types | ✔ Interior grade, exterior grade, softwood, hardwood |
| Manufacturing steps | ✔ Slicing, rotary cutting, gluing, Drying, attaching, finishing |
| Uses | ✔ Furniture production, shelving, windows, door shutter, flush door, wall furniture, wall panels, partition |
| Benefits | ✔ Strength, stability, moisture resistance, cost-effective, easy to work with, lightweight |
| Drawbacks | ✔ Not as durable as other materials, challenging to work with voids, susceptible to insect damage |
| Applications | ✔ Furniture, doors, wall panels, partition walls, flooring, other woodworks, railway carriages, interior decoration, prefabricated houses, bus bodies |
| How to choose | ✔ Consider thickness, core material, grade, veneer quality, design, sustainability, and budget. |
| How to work with | ✔ Cut to size, drill pilot holes, countersink screws/nails, sand, Finish |
| Comparison with plywood | ✔ Similar in properties, but plywood is more expensive |
| Comparison with MDF | ✔ Similar in properties, MDF is more costly and less moisture-resistant. |
| Waterproof | ✔ No, but it is more moisture-resistant than regular wood |
| Fire-resistant | ✔ It is more fire-resistant than stable wood but not entirely fireproof |
2. What is a Blockboard?
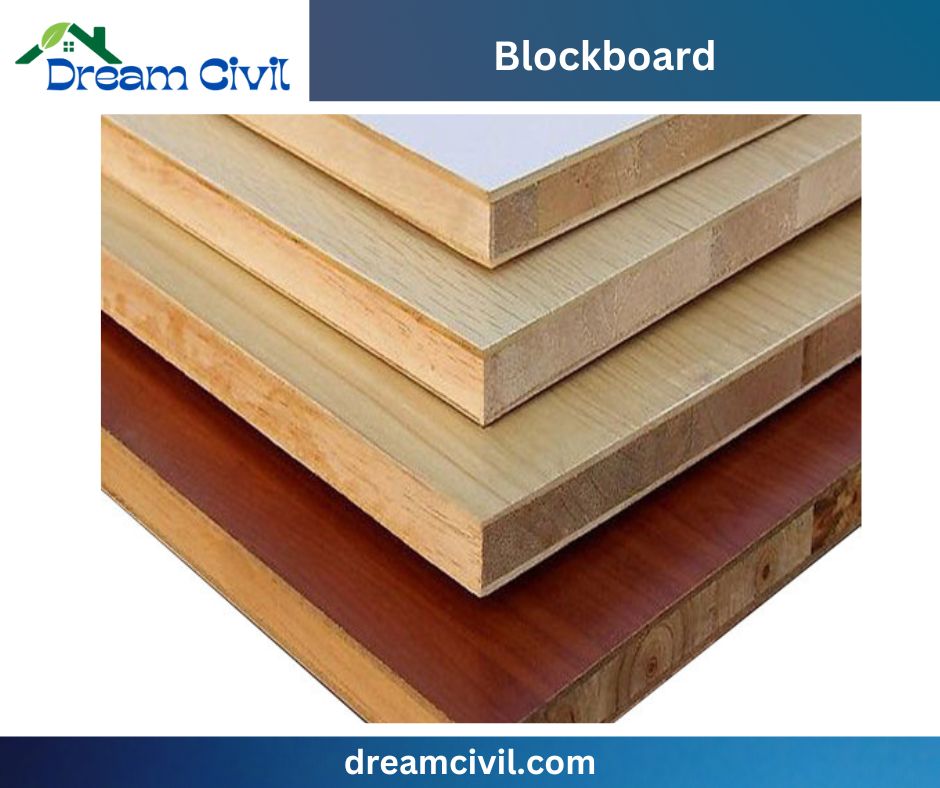
✔ Blockboard may be defined as an engineered compound plywood board where softwood strips are attached edge to edge and bonded jointly, machining generally a sandwich structure setting Hardwood between them.
✔ Blockboard is majorly available in various sizes and thicknesses. The standard length of the block board is 2440 x 1220 x 30 mm.
3. Technical Properties of Blockboards

The technical properties of block boards are as follows:
✔ Modulus of elasticity long
✔ Density
✔ Bending strength
✔ Bending strength cross
✔ Formaldehyde emission
✔ Modulus of elasticity cross
✔ Fire safety category
✔ Thickness tolerance
✔ Length and width tolerance
4. Types of Blockboards

✔ The classification of block boards mainly relies on various factors such as quality, use, and raw wood employed for the core.
The following are the types of block boards:
Depending on Quality and Use:
✔ Interior Grade Blockboard
✔ Exterior Grade Blockboard
Depending on the Raw Wood Used in the core:
✔ Softwood Blockboard
✔ Hardwood Blockboard
Various aspects of these types are well described below:
I. Interior Grade Blockboard
✔ These grades are produced for indoor services and are unsusceptible to moisture, Known ass MR (Moisture Resistant)—for example, Furniture, doors, and window shutters.
II. Exterior Grade Blockboard
✔ This type of block board is produced for outdoor uses. Exterior grades are known as BWP (Boiling Water Proof) or BWR (Boiling Water Resistant).
✔ This high resistance quality is because the adhesives employed here are also valuable for quality.
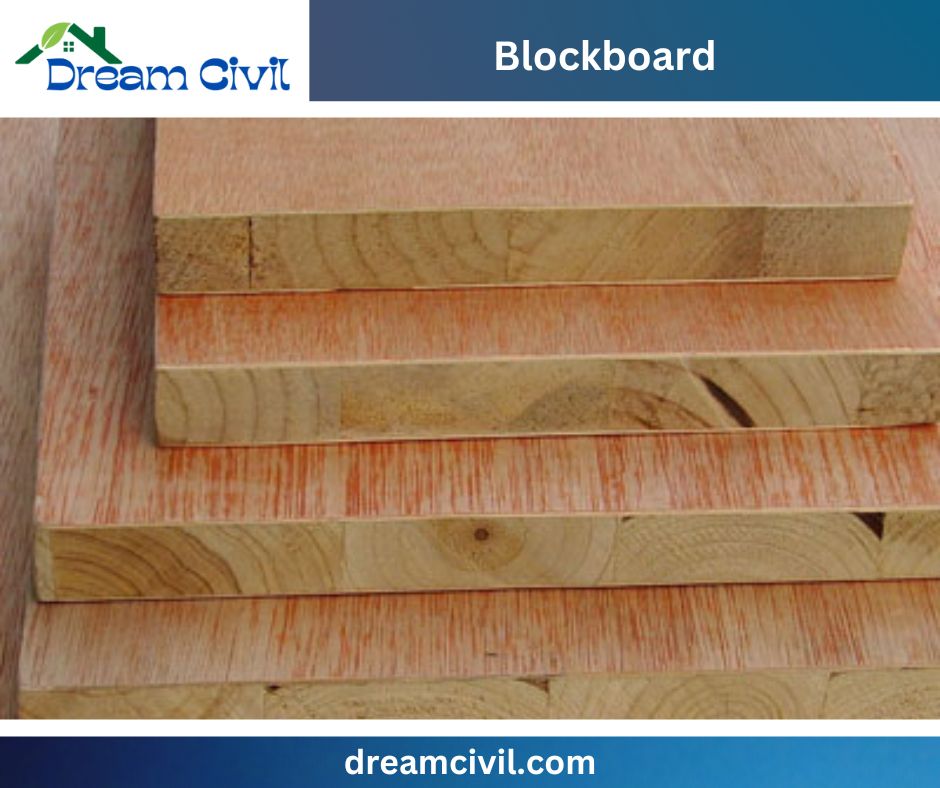
III. Softwood Blockboard
✔ Solid blocks of wood are employed to prepare each blockboard sheet attached jointly with operating Glue.
✔ The sheets are called strips or battens.
✔ The surface is coated with hardwood surfaces.
IV. Hardwood Blockboard
✔ Generally, Hardwood is dense, heavy, costly, and strong as the core is produced from rigid sheets.
✔ The layer is also made of Hardwood.
5. Manufacturing of Blockboard
The following are the steps of block board processing:
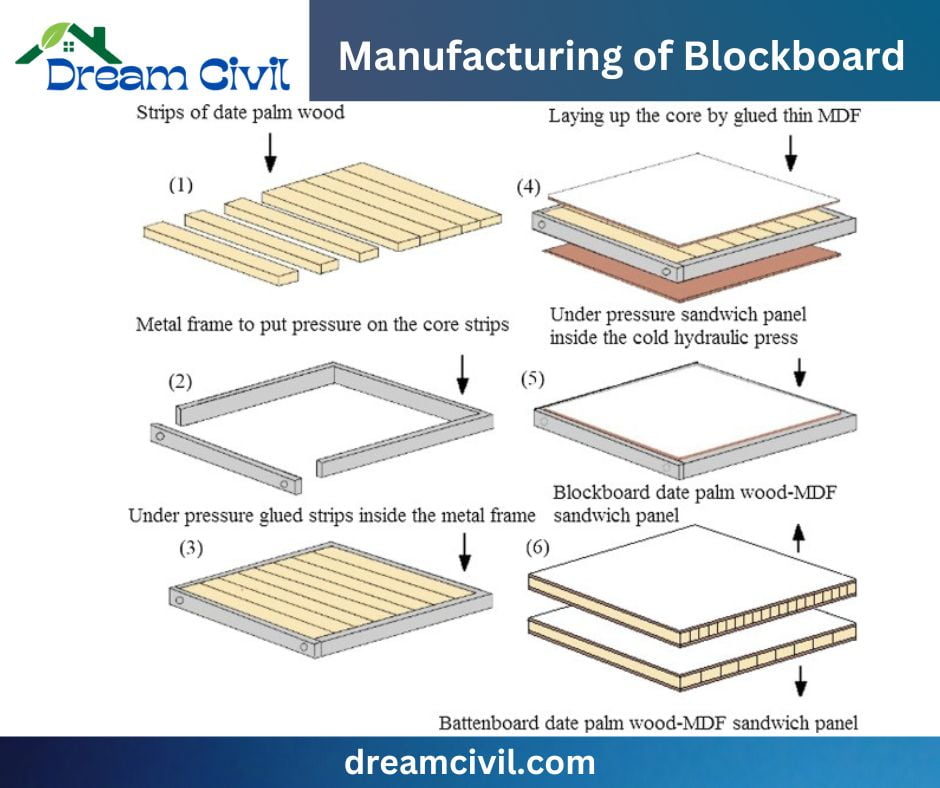
a. Slicing
✔ The timber logs are cut at first to make the raw blocks. The strips can be 25 mm.
b. Rotary Cutting
✔ For the outer layer, logs are trimmed at rotary cutting. Thus, veneer for coating is acquired.
c. Gluing
✔ Glue or adhesives connect the pieces, such as Urea-formaldehyde and phenol formaldehyde, a plastic resin.
✔ The exterior grade block board needs phenol-formaldehyde. Gluing is accomplished under high pressure.
d. Drying
✔ The blocks are dried to decrease the moisture and water content left inside them blocks. For Drying, the blocks are preserved before the sun.
✔ The moisture content is decreased to 10-12%. After appropriate Drying, they are prepared to produce a sandwich.
e. Attaching
✔ Blocks are connected employing softwood or Hardwood as needed for interior or exterior grade.
f. Finishing
✔ Last finishing offering lamination, a coating is accomplished.
6. Uses of Blockboard
The uses of Blackboard are as follows:
✔ For furniture production such as tables, benches, beds, etc.
✔ For shelving, such as extended bookshelves and worktops as heavier structures.
✔ For windows, door shutter, flush door.
✔ For preparing wall furniture.
✔ They do not slag in the middle or does not bend easily, so it is a selection for carpenters.
✔ For wall panels, partition.
7. Benefits of Blockboard

The benefits of blockboards are mentioned below:
✔ The soundness of blockboards is sufficient stability. These can offer peace in humid surroundings that possess moisture resistance.
✔ They are cheap.
✔ Using Glue, It can carry varnish, paint, and laminate coat on the surface. Block boards are suitable for screwing and nailing.
✔ Warping or twisting is the right option for its opposition quality.
✔ They can have screws, nails, and laminating coat; for this, it is comfortable to work on.
✔ Carpenters can efficiently employ their wood processing tools for block boards.
✔ The lightweight Blockboard produced is suitable to employ. The bulk of the board comprised of core blocks is also famous for its light as made from softwood and is effortless to transport.
✔ BWP, one type of Blackboard, is more robust, adequate, and invulnerable to water and humidity.
8. Drawbacks of Blockboard
The followings are drawbacks of blockboards are mentioned below:
✔ They are light in weight, so they are not largely reliable hard materials.
✔ They are more vulnerable and don’t have long durability.
✔ The undesirable void between softwood strips makes it challenging to work for carpenters.
✔ Screwing and nailing should be accomplished carefully; otherwise, it may break.
✔ Shrinkage and swelling of the board may appear.
✔ The breakdown of the blocking board is not secured.
✔ If the strip’s inner is cheap, low-quality wood may be damaged by insects.
9. Applications of Blockboard
✔ To construct various furniture pieces such as benches, sturdy tables, bookshelves, and sofas.
✔ To design both regular doors and flush doors with a solid core.
✔ In wall panels
✔ In partition walls
✔ In flooring
✔ In other Furniture like tables
✔ In the woodwork of railway carriages
✔ In interior decoration
✔ In prefabricated houses
✔ Bus Bodies
10. How do you choose the right Blockboard?

Before choosing the Blockboard, consider some points explained below:
Thickness: When selecting a Blockboard, it is essential to consider the appropriate thickness for its intended use. A thicker Blockboard is necessary for furniture-making purposes than for making a shelf. There are so many consistency options obtainable to suit diverse applications.
Core Material: It is generally believed that the Hardwood core blockboard is considered the strongest, most durable, and most stable type of Blockboard
Grade: Choose the correct rate of Blockboard for your intended use and environment. Consider BWR-grade for moisture-prone areas.
Veneer Quality: A high-quality veneer is paramount for a blockboard with a fantastic appearance and better durability.
Design and Aesthetics: Selecting a veneer that complements your project’s design, considering its appearance and grain pattern, is highly recommended.
Sustainability: When it comes to sustainability, it’s essential to opt for blockboards accepted from forests that are responsibly collected and maintain certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council).
Budget: To discover the right Blockboard, assume the core material, veneer quality, and thickness. Set a budget and look for reasonable options that meet your needs without sacrificing quality.
11. How do you work with a blockboard?
Material needed to work with Blockboard:
✔ Saw
✔ Drill
✔ Screwdriver
✔ Hammer
✔ Chisel
✔ Sandpaper
✔ Wood glue
✔ Finish of your choice (paint, stain, etc.)
Steps to work with a Blockboard:
✔ Cut the Blockboard to size
✔ Drill pilot jams before screwing or nailing
✔ Utilize a countersink bit to countersink screws/nails
✔ Sand the Blockboard before finishing
✔ Lay the Finish of your choice
✔ Slice across the grain when cutting BBlockboard✔ Operate suitable screws/nails for structural use
✔ Determine the best Finish for your project
12. How does Blockboard compare to plywood?

| Characteristic | Blockboard | Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Core | ✔ Softwood or hardwood strips | ✔ Thin layers of wood |
| Veneer | ✔ Yes | ✔ Yes |
| Strength | ✔ Good | ✔ Good |
| Stability | ✔ Good | ✔ Good |
| Weight | ✔ Lightweight | ✔ Medium weight |
| Cost | ✔ Relatively inexpensive | ✔ It is more expensive than Blockboard |
| Ease of workability | ✔ Easy to work with | ✔ Easy to work with |
13. How does Blockboard compare to MDF?
| Characteristic | Blockboard | MDF |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | ✔ A blockboard consists of softwood or hardwood strips sandwiched between two layers of veneer. | ✔ Wood fibers bonded together with resin and heat. |
| Strength | ✔ Good | ✔ Good |
| Stability | ✔ Good | ✔ Good |
| Weight | ✔ Lightweight | ✔ Medium weight |
| Cost | ✔ Relatively inexpensive | ✔ It is more expensive than BBlockboard |
| Ease of workability | ✔ Easy to work with | ✔ Easy to work with |
| Moisture resistance | ✔ Moderate | ✔ Low |
14. Is the Blockboard waterproof?
✔ The manageable weight and portability of the Blockboard make it advantageous for transportation.
✔ The core blocks, mainly consisting of softwood, count to its ease of movement. The BWP blockboard is sturdy and trustworthy and can endure water and humidity.
15. Is Blockboard fire-resistant?
✔ It’s worth noting that Blockboard is more fire-resistant than regular wood but not entirely fireproof.
✔ This is because the veneer on its surface acts as a barrier that protects the core from burning.
✔ However, it’s crucial to remember that a blockboard can still catch fire if exposed to high temperatures or flames.
✔ Additionally, the level of fire resistance will vary depending on the type of wood used in both the core and veneer layers.
Read Also: Types of Concrete Admixtures
| Verified By: Er. Bipana Kshetri Puri |

