Table of Contents
Crops refer to plants grown by farmers.
Crops are classified into different categories based on agricultural use, seasons, life cycle, etc.
1. Types of Crops Classification
i. Agricultural classification of crops
a. Field crops: Wheat, Rice, Maize, Barley, etc.
b. Plantation Crops: Tea, Coffee, Coconut, etc.
c. Commercial Crops: Oilseed, Cotton, Sugarcane, Groundnut, etc.
d. Horticulture: Fruits and vegetables.
e. Forage Crops and Grass: Fodder.
f. Miscellaneous Crops: Silk, Medicinal crops, etc.
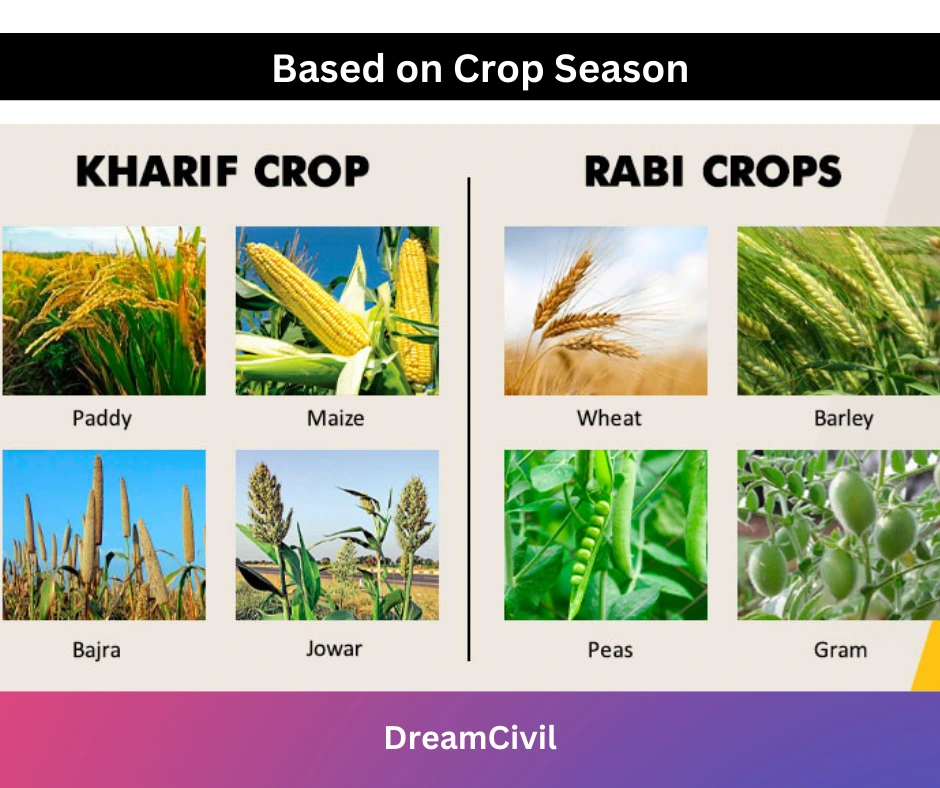
ii. Classification of crops based on crop season
A. Rabi crops:
✔ Rabi season starts in October and ends on 31st March.
✔ The crops which are sown in the winter season are called Rabi crops. So they are also called winter crops.
✔ Rabi crops are Wheat, Linseed, Mustard, Potatoes, etc.
B. Kharif crops:
✔ Kharif season starts from 1st April to 30th September.
✔ The crops which are sown in the summer season are called Kharif crops. They are also called summer crops.
✔ Kharif crops are Rice, Maize, Cotton, Tobacco, Ground Nut, Millet, etc
C. Perennial crops:
The crops sown in Summer & winter, i.e., throughout the year, are called perennial crops. E.g., Sugarcane.

iii. Classification of crops based on the life cycle (Ontogeny)
There are three types of crops based on the life cycle.
a. Annual Crops
~ Annual crops complete their lifecycle within a year or a season.
~ They grow, bloom, produce seeds, and die within a season.
~ Examples: Tomatoes, Capsicum, Cucumber, Peanuts, All sorts of grains, mustards, sunflowers, wheat, maize, eggplants, lettuce, etc
b. Biennial Crops
~ They complete their natural lifecycle in two consecutive seasons or two years.
~ In the first year, vegetative growth occurs (mainly the development of stems, leaves, etc.).
~ In the second year, they produce flowers and seeds. Then the plant dies.
~ Examples: Carrots, Raddish, Cabbage, Onions, Beet Root, Sugar Beet, etc.
c. Perennial Crops
~ They complete their natural lifecycle in three or more years.
~ These crops may be seed-bearing or non-seed bearing.
~ Examples: Apple, Pear, Peaches, Walnuts, Coconut, etc.
~ They generally occupy the land for more than 30 months.
iv. Classification of crops based on climate
a. Tropical Crop: Sugarcane, Coconut
b. Sub-Tropical Crop: Rice Cotton
c. Temperate Crop: Barley, Wheat
d. Polar Crop: Pasture Grasses, All pines
v. Classification of crops based on the commercial field
a. Food Crops: Maize, Soyabean, Wheat, Barley, Millet, Groundnut, etc.
b. Fooder / Forage Crops: Stylo, Fodder Maize, Oats, Fodder Millet, etc.
c. Commercial / Industrial Crops: Tobacco, Sugarcane, Cotton, Jute, etc.
d. Food Adjuvants: Alum, Garlic, Cumin, etc.
vi. Classification of crops based on a range of cultivation
a. Garden Crops:
They are generally grown on small scales in the garden—examples: Onion, Turmeric, Garlic, etc.
b. Plantation Crops:
They are grown in a large area. These crops are perennial- for example= Tea plants, Coffee plants, Rubber plants, etc.
c. Field Crops:
They are seasonal crops like wheat, millet, barley, etc.
2. Some Terminologies
✓ Arid region:
The region where irrigation is a must for agriculture is called the arid region.
✓ Semi-arid region:
The region where inferior crops can be grown without irrigation is called the semi-arid region.
✓ Crop Period:
The period from the instant of sowing crops to the moment of Harvesting is called the crop period. It is also called a growing period.
Crop period = Harvesting date-Sowing date.
3. Total Growing Period of Crops
✓ The total growing period (in days) is the period from sowing or transplanting to the last day of the harvest.
It is principally passionate about the sort of crop, the selection of the climate & the planting date.
✓ Generally, it is often assumed that the growing amount for a definite crop is longer once the climate is cool and shorter once it is heating.
INDICATIVE VALUES OF THE TOTAL GROWING PERIOD
| Crop | Total growing period (days) | Crop | Total growing period (days) |
| Banana | 300-365 | Millet | 105-140 |
| Cabbage | 120-140 | Pepper | 120-210 |
| Carrot | 100-150 | Potato | 105-145 |
| Citrus | 240-365 | Radish | 35-45 |
| Cotton | 180-195 | Rice | 90-150 |
| Cucumber | 105-130 | Sorghum | 170-130 |
4. References1. Content Filter & Authenticity Checking Team, Dream Civil International (Our team checks every content & detail to maintain quality.) |
| Read More: Duty in Irrigation |
