Table of Contents
A surge tank may be defined as a water storage device that is utilized for a purpose of a pressure neutralizer in a hydropower water conveyance system to withstand excess pressure rise and pressure drop conditions.
1. Location of Surge Tanks
The location of the surge tank is also important to produce better results. It should be located in such a way that
a. Surge tanks are placed near the powerhouse to decrease the length of penstocks.
b. No limitations are kept for surge tank height.
c. Location at which flat-sloped conduit and steep-sloped penstock meet.

2. Use of Surge Tank
The main works of the surge tank are as follows
a. It should prevent the conduit system from high internal pressures.
b. It should help the hydraulic turbine regarding its regulation characteristics.
c. It should hold the water to raise the pressure in the pressure drop
3. Types of Surge Tank
Various types of surge tanks used in the hydropower water conveyance system are as follows.
a. Simple surge tank
b. Inclined surge tank
c. Differential surge tank
d. Restricted orifice Surge tank
e. Gallery Surge tank
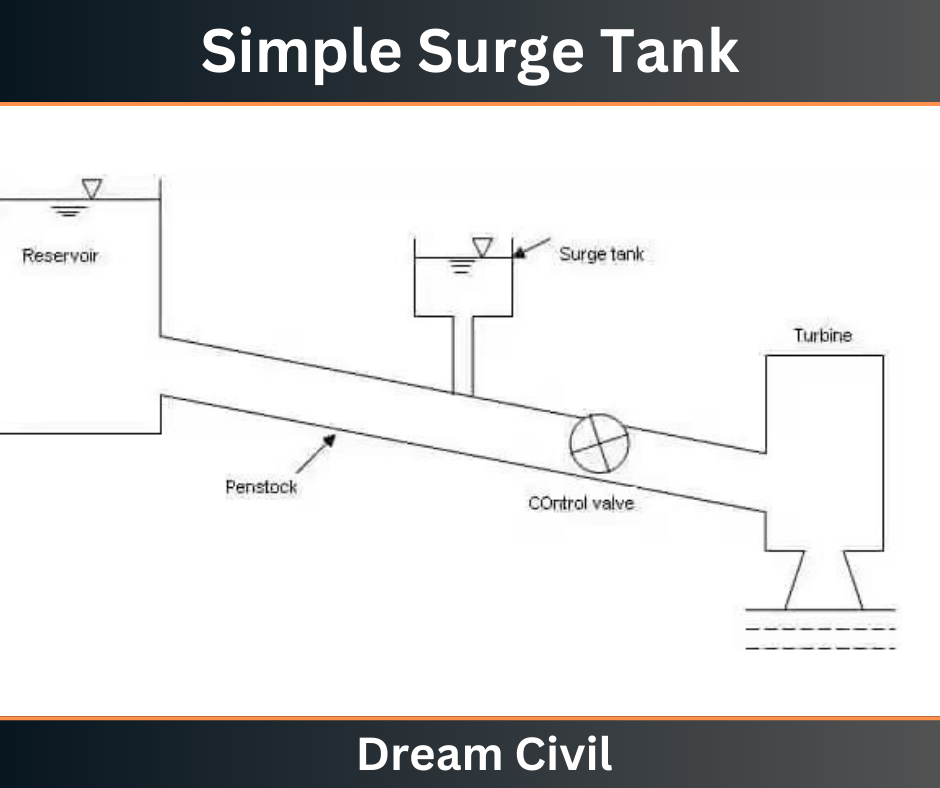
a. Simple Surge Tank
A simple surge tank is like a vertical pipe that is connected between the penstock and turbine generator. These are built with huge heights and holds are also given to support the tank. Whenever the water flow is quickly increased the water is held in the surge tank and balances the pressure.
The top of the surge tank is opened to the atmosphere, If the surge tank is filled fully then it overflows to balance the pressure neutralization.
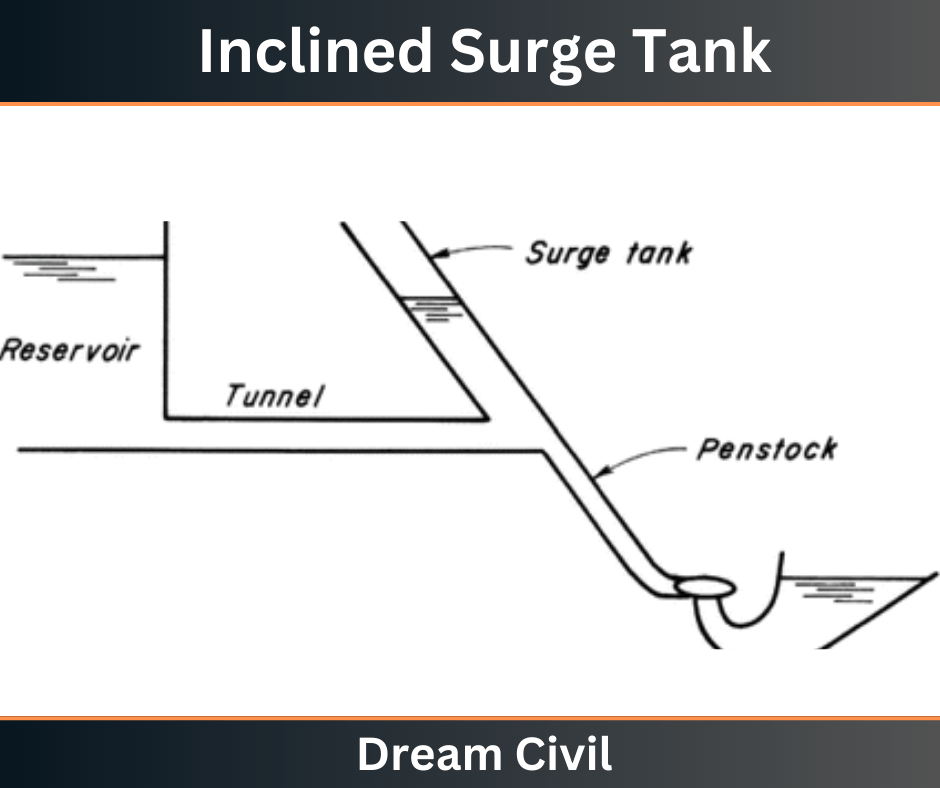
b. Inclined Surge Tank
An inclined surge tank, surge tank is given with some inclination. It is provided when there is a restriction on the height of the tank. By constructing an inclined surge tank the overflowed water under excess pressure is moved into the inclined tank and pressure canceled
c. Differential Surge Tank
A differential surge tank is provided with an internal riser fixed in the tank. This riser has a small diameter through which water moves into the riser when it overflows. The riser also has annular holes at its lower end.
These holes support the flow into or out of the tank. So, the excess pressure is canceled by the internal riser of the surge tank, and storage of water is performed by the outer tank. So, it is called a differential surge tank.

| Read More: Sedimentation Tank Numerical |
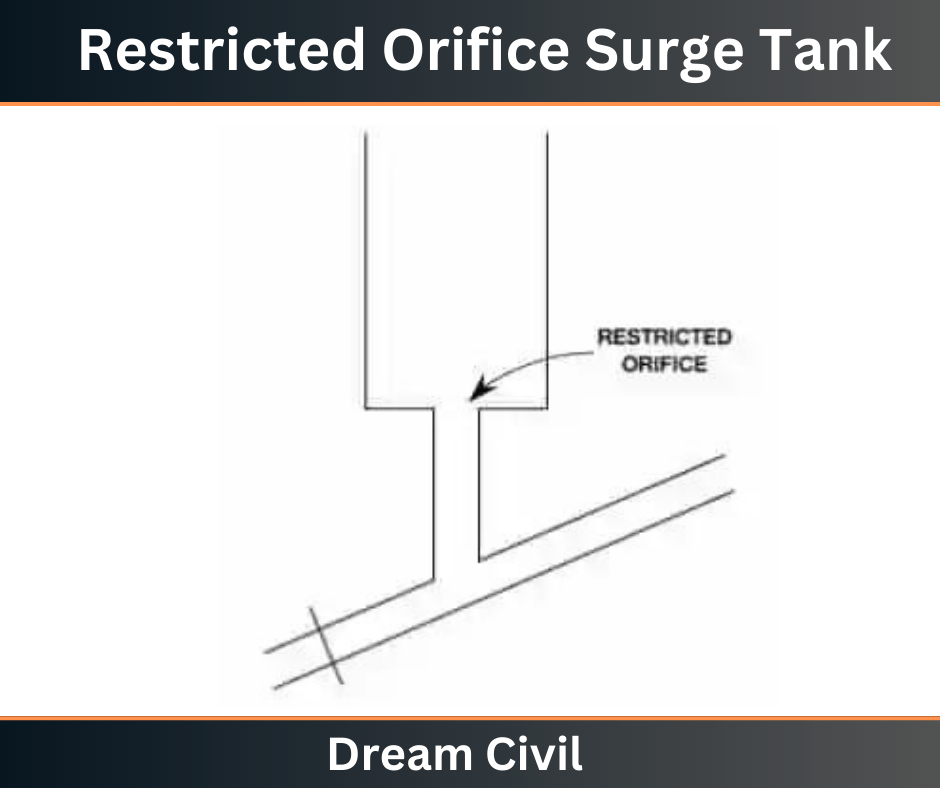
d. Restricted Orifice Surge Tank
The restricted orifice has an orifice between the pipeline and surge tank. This orifice is also called a throttle so, it is also called a throttled surge tank. This throttle or orifice has a small diameter.
If the water overflows it should move into the surge tank through this orifice because of the small diameter, frictional losses will be created and excess pressure in the main pipeline is canceled out.
This will develop rapidly a retarding or accelerating head in the pipe. To decrease the water hammer effect, the diameter of the orifice should be constructed well designed for full rejection of load by the turbine.
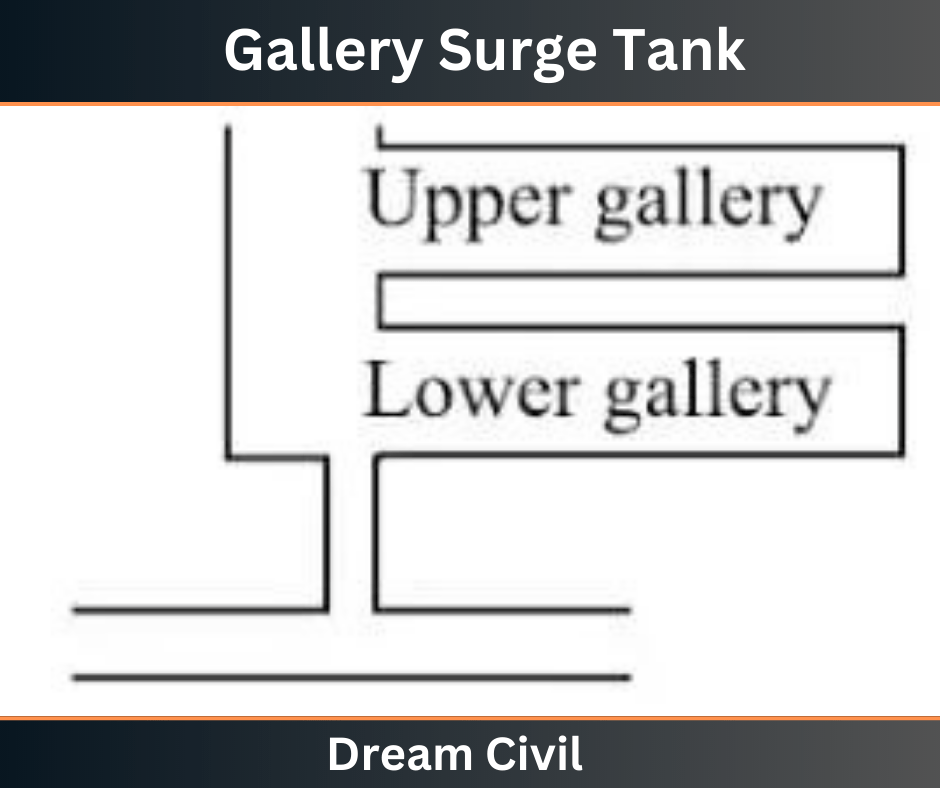
e. Gallery Surge tank
The gallery-type surge tank has surplus storage galleries. These storage galleries are also known as expansion chambers. So, gallery-type surge tanks can also be described as expansion chamber-type surge tanks.
These expansion chambers are usually kept below and above the surge levels. Below surge, level chambers are utilized to hold more water in them and released when it is needed or there is a short drop in pressure. Upper surge level chambers are utilized to soak up the excess pressure.
4. References1. Content Filter & Authenticity Checking Team, Dream Civil International (Our team checks every content & detail to maintain quality.) |
.

