Table of Contents
| In this article, we will discuss the specific gravity of soil and the process to determine it. |
What is Specific Gravity?
The specific gravity of soil may be defined as the ratio of the mass of solids to the mass of an equivalent volume of water at 4ºC.
The value of specific gravity (soil) varies between 2.65-2.80.
Mathematically,
G = Ms / Mw = ρs / ρw = γs / γw
Where,
ρs = Density of Solid
ρw = Density of Water
γs = Unit Weight of Solid
γw = Unit Weight of Water
A specific gravity test is necessary to get an idea of various soil properties such as void ratio, degree of saturation, etc.
1. Relationship of Specific Gravity of Soil, Void Ratio, Porosity, Water Content & Degree of Saturation

2. How can we determine the Specific Gravity of Soil?
A pycnometer or constant volume method has been found to be most reliable for the determination of specific gravity.
Specific Gravity Determination By Pycnometer Method
Apparatus Required:
1. Pycnometer

Fig: Pycnometer
2. Weighing Balance with a weighing accuracy of 1gm
Procedure:
The laboratory procedure for determining the specific gravity of soil by pycnometer method can be listed as follows:
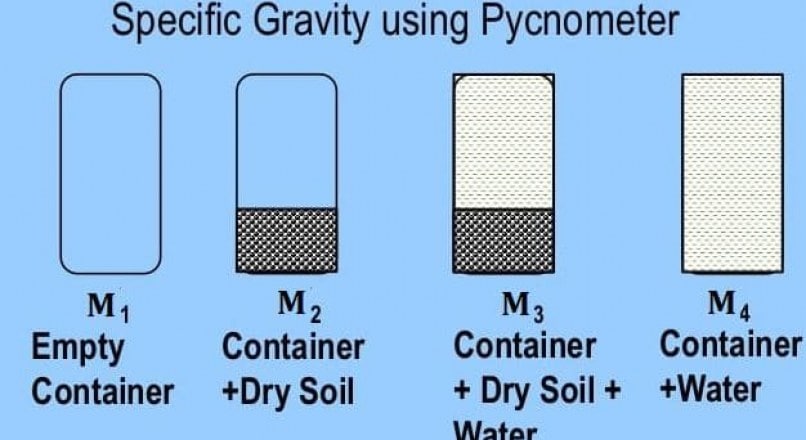
1. Find the mass of the empty pycnometer say M1.
2. Fill pycnometer with about 200 gm of dry sample and take its weight say M2.
3. Add water to the pycnometer such that it is half full of water. The air in the soil sample is completely expelled by heating or suction.
Then the water is added to its full capacity and the pycnometer is weighed and say M3
4. Empty the pycnometer of all its contents and clean it. Next, the pycnometer is filled with water only and its weight is determined say M4.
Calculation:
G = [M2-M1] / [ (M2-M1) – (M3-M4)]
Where,
G = Specific Gravity
M1 = Mass of empty container
M2 = Mass of Container + Dry Soil
M3 = Mass of Container + Dry Soil + Water
M4 = Mass of Container + Water
| Read Also: Types of Pipes in Civil Engineering & Construction |
