Table of Contents
✔ Dumpy levels are simple and reliable surveying instruments for measuring horizontal angles and elevations. They are essential for construction, surveying, engineering, and other applications. Learn more about how dumpy levels work, their applications, and their advantages and disadvantages in this comprehensive guide.
1. What is a Dumpy Level?

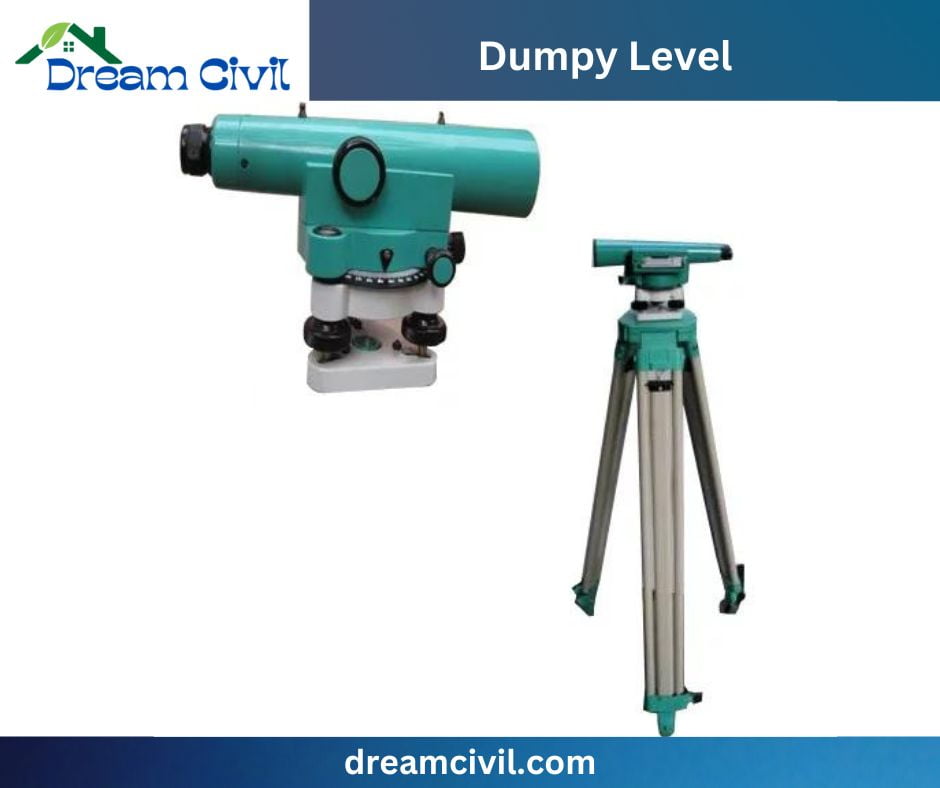
✔ The dumpy level is an excellent tool for those in construction or surveying. Its uncomplicated design, featuring a rotating telescope with a crosshair, allows for easy measurement of heights at different points.
✔ By setting it up at a known elevation and leveling the telescope, you can quickly and accurately measure the height of any point you need. This straightforward yet efficient tool is necessary for any construction site or surveying application.
✔ The dumpy level may be an optical instrument for surveying and leveling operations. It contains a telescope tube firmly placed between two collars and adjusting screws. The vertical spindle presents the complete device. The telescope on the dumpy level can be rotated along the horizontal plane.
✔ The relative elevation of survey points on the land can be calculated with the help of the dumpy level. In 1832, Willian Gravatt invented the dumpy level. He was a civil engineer; he created the dumpy level while working with the Y (Wye) level instrument.
2. How Does a Dumpy Level Work?
| Step | Description | Optical Principles |
| Leveling the Instrument | ✔ The Dumpy Level is carefully leveled on a tripod to ensure accurate measurements. | Leveling: The telescope is horizontal when the bubble is centered in the level. |
| Viewing the Target | ✔ The surveyor aims the telescope’s crosshairs at the target. | Refraction: The objective lens bends light to focus the target image on the focal plane. |
| Sighting the Target | ✔ The telescope sights the target, a marked rod at the measurement point. | Sighting: The crosshairs in the telescope are used to sight the target precisely. |
| Reading the Measurement | ✔ The surveyor centers the crosshairs on a numbered graduation on the staff to determine the line of sight. | Measurement: The surveyor measures the line of sight elevation by aligning the crosshairs with a numbered graduation on the staff. |
| Taking the Measurement | ✔ The staff reading at the crosshairs is the height difference from the reference plane. | Calculation: The height difference is calculated by subtracting the staff reading from the instrument height. |
3. Dumpy Level Errors
| Error Type | Description |
| Instrumental Errors | ✔ Instrumental errors are caused by the dumpy level’s construction or design flaws. |
| Collimation Error | ✔ Collimation error causes incorrect readings due to a misaligned telescope. |
| Index Error | ✔ Misaligned horizontal crosshair causes discrepancies in readings. |
| Reading Errors | ✔ Reading errors occur due to incorrect staff readings, misaligned crosshairs, or parallax errors. |
| Environmental Errors | ✔ Environmental factors can affect the accuracy of dumpy levels. |
| Leveling Errors | ✔ Leveling errors can introduce inaccuracies in measurements. |
| Instrument Stability | ✔ Instrument stability is essential for accurate measurements. |
| Distance Errors | ✔ Distance errors are more common in long-distance measurements due to the curvature of the Earth. |
| Operator Errors | ✔ Operator errors can lead to inaccurate measurements. |
4. Principle of Dumpy Level Instrument
✔ The dumpy level works on the principle by visually correlating two or more points through an attached telescope and a bubble level. A wise level of accuracy can be attained through these steps.
✔ It is also known as the Surveyors level and Builders level.
5. Applications of Dumpy Level

I. Construction: Dumpy levels ensure accurate elevation measurements for critical building components.
II. Surveying: Dumpy levels help surveyors create accurate maps for various applications.
III. Engineering: Dumpy levels enable engineers to design and build safe and reliable infrastructure.
IV. Agriculture: Dumpy levels help farmers optimize their irrigation and crop management practices.
V. Archaeology: Dumpy levels help archaeologists map and preserve ancient sites.
VI. Astronomy: Dumpy levels help astronomers observe and study celestial objects.
VII. Geology: Dumpy levels help geologists study and assess geological features and hazards.
6. Parts of Dumpy Level
1. Telescope
✔ The telescope in the dumpy level is utilized to compute distant objects in the line of sight. The telescope is built with a vertical spindle, giving the telescope to be movable in different directions.

The telescope comprises different elements, and all the details are as follows:
I. Eye Piece: It contains a magnifying glass and is essentially utilized by the observer.
II. Objective Piece: It is placed at the farther end of the eyepiece. It includes both a convex lens and a concave lens.
III. Diaphragm: It is provided in the eyepiece’s outline with a dark metal cross. They are given to intersect the objects.
IV. Focusing Screw: They are kept to align the focus and image clarity of the object.
V. Ray Shade: It prevents sunlight from passing through the objective lens.
2. Bubble Tubes
✔ They are provided to align the level of the instrument. Bubble tubes in horizontal and vertical directions within a built-on dumpy level. The device is perfect to survey when both the bubbles are in the middle.
3. Compass
✔ A compass is utilized to know the magnetic bearing of the line of the path of the survey. The compass contains a pointer that shows directions. The compass is ranged for the magnetic approach in the north order.
4. Vertical Spindle
✔ It is placed in the middle of the instrument. It supports the telescope and rotates in a vertical direction. A vertical Spindle is a conjunction point between a tripod and a telescope.
5. Tribrach
✔ Tribrach is parallel to the leveling head and is essentially utilized to manage the horizontal level of the instrument. The trivet is attached through foot screws.
6. Foot Screws
✔ The foot screws calibrate the instrument through the bubble tube. By adjusting foot screws, one can calibrate the tribrach plate. To make sure the bubble is in the middle, foot screws are used.
7. Levelling Head
✔ The leveling head is also known as a trivet; it contains two triangular plates lined up parallel to each other. It has groves to support foot screws.
8. Tripod
✔ Tripod is the platform for supporting the complete dumpy level. Tripod Contains three legs prepared of hollow steel sections or light or hardwood. Steel shoes at the foot ensure the Tripod is unmoveable with small jerks.

| Read Also: Total Station in Surveying |
7. Use of Dumpy level
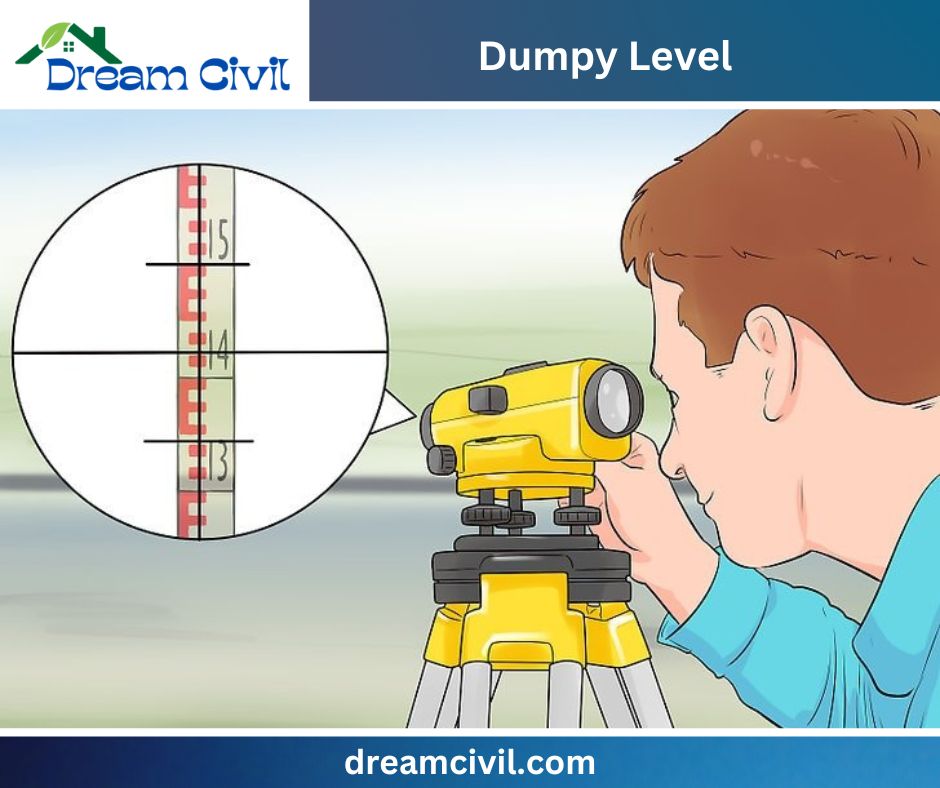
✔ It has enormous importance in the field of surveying a construction site. The accuracy and handiness of the dumpy level have been the best choice for the surveyors. The uses of dumpy level are as follows:
a. It is used as the main reason for executing leveling on a construction site to smooth the field level.
b. It is used to calculate the differences in height between two points.
c. It calculates the height and distance of various locations of surveying land through the principle of relativity.
d. It calculates the following distance amongst various points on the surveying land.
e. It is used to set out levels and inclined surfaces for construction.
f. It is used to prepare a contour on land.
8. Precautions While Setting Up Dumpy Level
All the essential precautions should be taken while handling the instrument. Otherwise, the error will be high. The protection that needs to be taken while working with a dumpy level.
✔ The Tripod should be managed to eye height.
✔ Avoid touching, pushing, or applying pressure on the Tripod while moving around or working.
✔ When moving around the Tripod, don’t trip over the legs.
✔ Watch the bubble every time; changes in a drop can give inaccurate results.
✔ Neglect setting up the instrument on soft ground.
9. Advantages of Dumpy Level
The advantages of dumpy level are as follows:
✔ Simpler construction with minimum movable parts.
✔ Minimum adjustments are to be made.
✔ High rigidity makes it versatile for long-duration surveys.
✔ High optical power.
✔ Cost-efficient in terms of usage on diversified construction sites.
10. Disadvantages of Dumpy Level
The disadvantages of dumpy level are as follows:
✔ Bounded to the site with horizontal angle measurement
✔ There can be a certain level of inconsistency in the values collected.
11. Dumpy Level vs. Auto Level
| Feature | Dumpy level | Auto level |
| Leveling | ✔ Manual | ✔ Automatic |
| Accuracy | ✔ Lower | ✔ Higher |
| Ease of use | ✔ More difficult | ✔ Easier |
| Price | ✔ Less expensive | ✔ More expensive |
| Read Also: Topographic Surveying |
| Verified by: Er. Bipana Kshetri Puri |

