Table of Contents
Road alignment selection is not just the selection of road geometry it is also an art. In horizontal alignment design, care should be taken for uniformity of procedure which should be fluent and blend well with the surrounding topography, it is necessary to provide smooth and flowing alignment which confirms natural contours because straight or rigid alignment damages the environment, and destroys natural slopes and disturbs plant growth. Due consideration should be given to the conservation of existing features while selecting alignment.
1. Alignment Design
Road landscaping, environmental considerations, and social aspects are the other factors that should be considered in alignment selection Followings are the recommendations as per IRC Special Publication no 21-1979.
a. Avoid long tangents exceeding 3 km.
b. Curvilinear alignments with long curves are better from both safety and aesthetic aspects.
c. Avoid sharp curves.
d. Proportioning of curves.
e. The reverse of curves and compound curves should be avoided as far as practicable.
f. In reverse curves, a sufficient length of tangents accommodates the required transition length.
g. The road shall be perceived by motorists as a three dimension entity.

2. Sitting of bridges
For major bridges above 300m, proper sitting of bridges should be the principal consideration.
For small bridges, less than 60 m, fluency of the alignment should govern the choice of the bridge location.
For spans between 60-300 m, the designer should use his discretion keeping in view the importance of the road, overall economic considerations, and aesthetics.
In selecting vertical alignment, the followings are some of the recommendations.
a. Grade changes shouldn’t be too frequent.
b. No change in grade within a distance of 150m.
c. Avoid short valley curves.
d. Avoid broken back-grade lines.
e. Continuity in profile;.
f. Avoid saw-tooth profile.

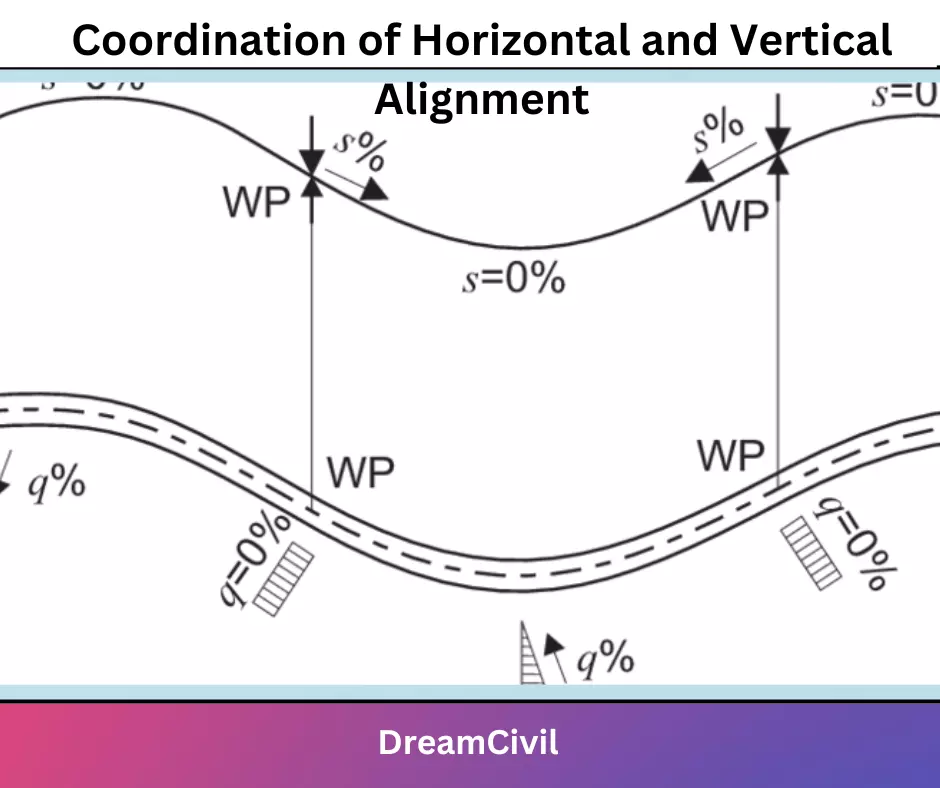
3. Coordination of Horizontal and Vertical Alignment
√ The plan and profile of the road should be designed in close coordination of each other to produce a three-dimensional effect.
√ Road architecture.
√ Ensure safety, improve the utility of the highway and contribute to the overall aesthetics.
√ Internal harmony
√ Proper combination of road elements
√ External harmony.
√ Combination of external elements like trees, buildings, etc in road design for a better look.
Read Also: Culvert Spillways Vs Siphon Spillways