Table of Contents
A. What are smart cities?
Smart cities are cities that use digital solutions to improve infrastructure and benefit residents and businesses while reducing resource consumption and emissions.
B. What are the latest trends in innovative city development?
The latest trends in innovative city developments are:
1. Sustainable Urban Planning

As urban areas develop, prioritizing sustainability in their planning is becoming increasingly common.
This involves incorporating green spaces, promoting eco-friendly modes of transportation, and constructing energy-efficient buildings.
Resilient designs and green infrastructure are also being implemented to address climate change.
2. Smart Mobility

Ingenious mobility solutions, such as electric and autonomous vehicles, bike-sharing programs, and enhanced public transportation systems, also accumulate favor.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) outlets offer seamless, multi-modal transportation options.
3. Data-Driven Governance

Cities are using data analytics and AI for informed decision-making in governance.
Data-driven traffic management, predictive policing, and personalized city services are examples.
The purpose is to sweeten efficiency, cut costs, and enhance the urban experience.
4. Digital Twin Technology

Cities are creating virtual replicas of themselves using digital twin technology for modeling and simulating various scenarios.
They can be operated for urban planning, infrastructure development, and emergency response.
5. Sustainable Architecture

Sustainable architecture is a growing tendency, with visionary building textiles and designs that lessen energy consumption and emissions while sweetening indoor air quality.
6. Circular Economy Initiatives
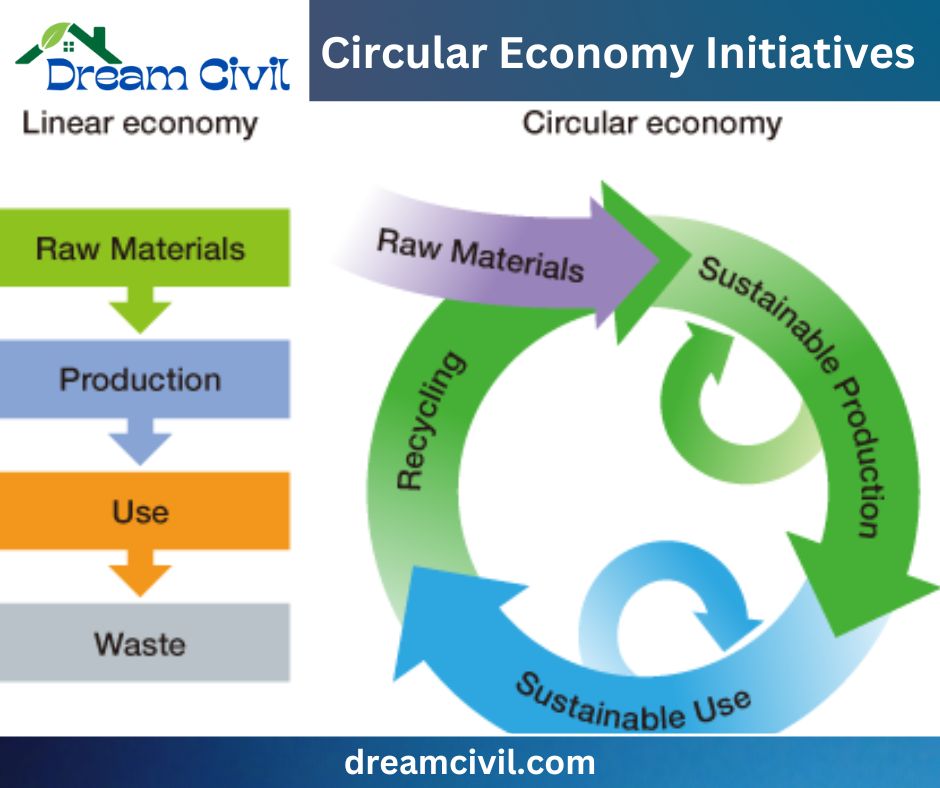
Circular economy initiatives, which encourage recycling and upcycling, are being promoted to minimize the environmental impact of consumer products.
7. Community Engagement

Community engagement becomes more paramount as citizens judge through digital outlets and participatory initiatives.
Citizen feedback and collaboration are seen as essential to successful city development.
8. Resilience Planning

Resilience planning is necessary for natural disasters and unforeseen events.
This includes adequate disaster preparedness, infrastructure that can resist harsh conditions, and the usefulness of renewable energy sources.
9. Affordable Housing Solutions

Housing affordability is an international concern, and cities are digging into innovative solutions like co-accommodation, micro-apartments, and modular construction to address the issue.
10. Health and Well-being

Post-pandemic, creating healthier cities is a top priority.
Ambitions include designing urban spaces for physical activity, sweetening air quality, and improving access to healthcare services.
11. Digital Inclusion

Digital inclusion is paramount, and cities are functioning to guarantee that all residents can access affordable high-speed internet.
Digital connectivity has become indispensable for education, employment, and daily life.
12. Alternative Energy Sources

Instilling renewable energy sources, like solar and wind power, is essential for cities to reduce their carbon footprint and promote sustainability.
C. What are the Case studies of successful innovative city projects?
Here are ten cities around the world that have successfully implemented innovative and sustainable solutions for urban living:
1. Copenhagen – Bicycle-Friendly City

With extensive bike lanes, bike-sharing programs, and other infrastructure, Copenhagen is becoming a leader in boosting cycling as a sustainable method of transportation.
2. Singapore – Smart Nation Initiative

Singapore’s Smart Nation Initiative leverages technology and data to enhance the quality of life for its citizens, including intelligent traffic management and e-governance.
3. Songdo – Smart and Sustainable City

Built with sustainability and technology in mind, Songdo features smart buildings, waste management systems, and efficient transportation networks.
4. Masdar City – Sustainable Urban Development
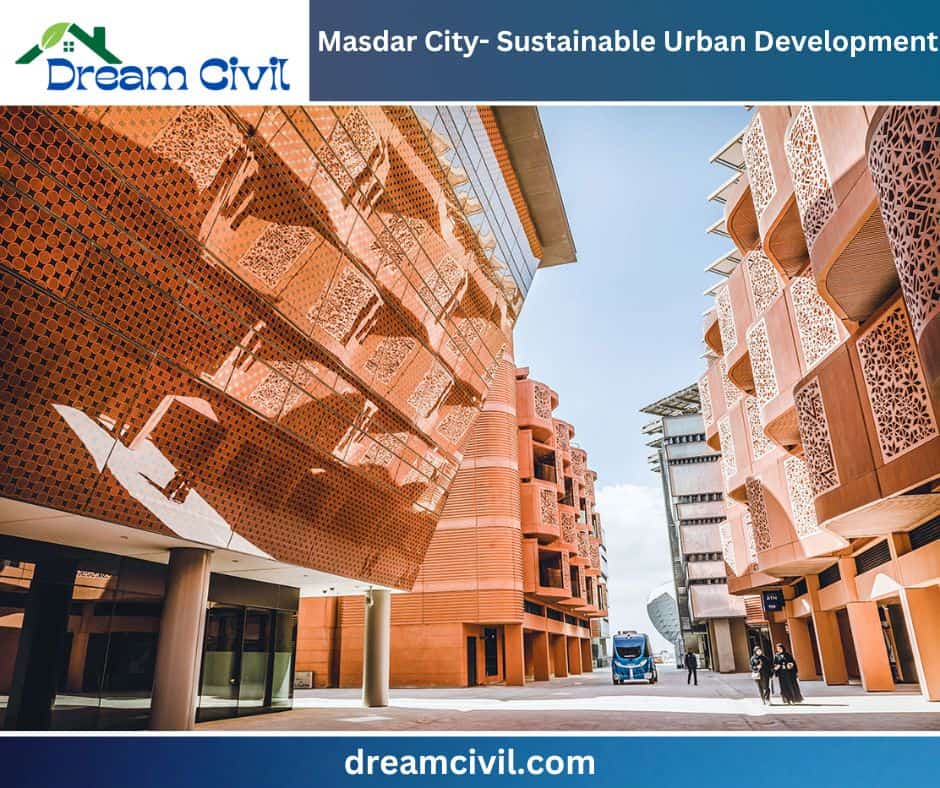

Masdar City focuses on renewable energy and green technology, utilizing solar power and sustainable architecture and planning.
5. Medellín – Urban Transformation

Through initiatives like escalators in hilly neighborhoods, cable cars, and improved public spaces, Medellín has transformed its urban landscape.
6. Barcelona – Smart City Solutions

Barcelona has implemented innovative city solutions, such as intelligent waste management and digital citizen services, to improve efficiency and sustainability.
7. Portland, Oregon – Sustainable Transportation

Portland has eco-friendly transportation options like light rail, streetcars, and bike lanes.
8. Amsterdam – Smart Mobility

Innovative mobility solutions, including a dynamic traffic management system and an integrated platform for transportation modes, have been implemented in Amsterdam.
9. Bristol – Smart Energy
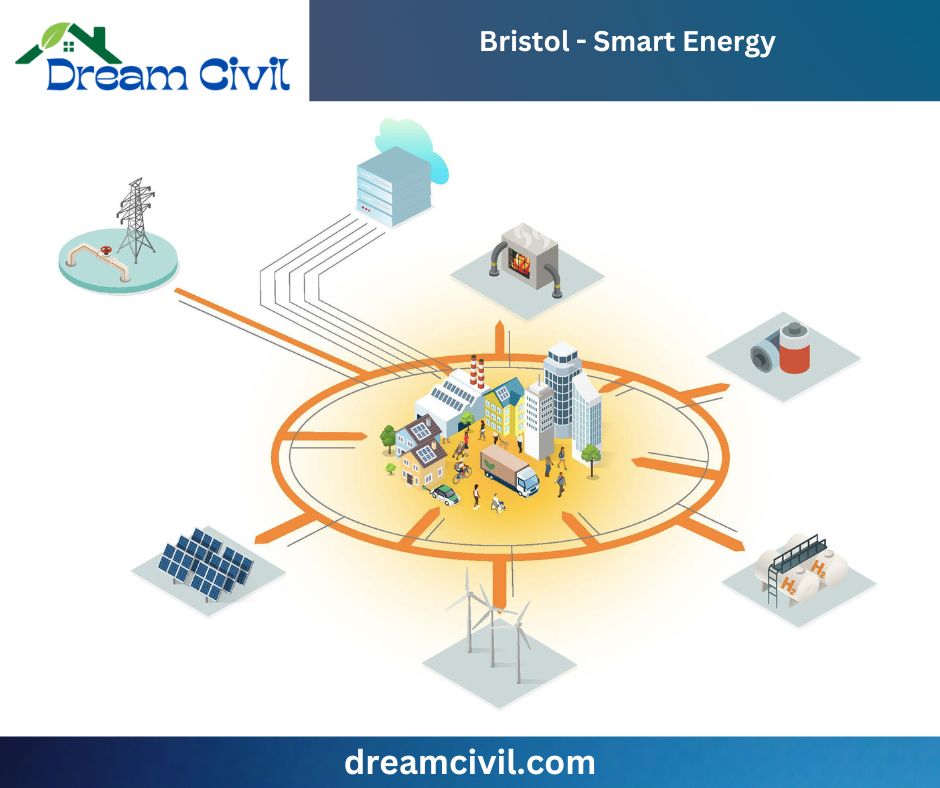
Intelligent energy solutions, such as a local marketplace for renewable energy, have been promoted in Bristol to ensure energy sustainability and community engagement.
10. Seoul – Digital Governance

Seoul’s e-government initiative has improved government services and transparency, allowing citizens to access various services online.
D. What are Expert opinions on smart cities?
Smart cities have been discussed and analyzed among specialists with varying opinions. Nonetheless, some common themes and philosophies have emerged. In the following, you will find crucial expert views on smart cities.
1. Improvement in Quality of Life

Smart cities can significantly sweeten inhabitants’ grade of life by incorporating technology and data into urban planning.
By doing so, transportation can be enhanced, pollution can be diminished, public safety can be enriched, and access to fundamental services can be provided.
2. Sustainability and Environmental Benefits

Intelligent cities are indispensable in global efforts to battle climate change.
Experts suggest intelligent urban planning can reduce energy consumption, lower emissions, and more sustainable resource use.
3. Economic Growth and Innovation

Innovative city initiatives can stimulate economic growth by attracting tech companies and startups.
Technology infrastructure and invention acquisitions can lead to job creation and economic development.
4. Improved Public Services

Smart cities can enhance public services’ efficiency and effectiveness.
Governments can make additional knowledgeable decisions and offer services more effectively using data analytics, IoT, and AI.
5. Data Privacy and Security

Experts emphasize addressing data privacy and security concerns in smart cities.
As cities assemble extensive amounts of data, there is a need for concentrated cybersecurity criteria and straightforward data governance policies to protect citizens’ information.
6. Digital Inclusion

Ensuring all residents can access digital services is crucial.
According to experts, bridging the digital spine and equipping impartial credentials to technology and the internet are essential.
7. Community Engagement

Innovative city initiatives should involve residents in decision-making.
Community engagement is vital for the success of innovative city projects as it helps ensure that the initiatives align with the population’s needs and preferences.
8. Interoperability and Standards

Developing interoperability standards is necessary to ensure that various intelligent city technologies work together seamlessly.
Standardization can help avoid fragmentation and improve the scalability of smart city solutions.
9. Resilience and Disaster Preparedness

Building resilience against natural catastrophes and other troubles is a priority.
Experts say innovative city technologies can be paramount in disaster preparedness and response.
10. Long-Term Sustainability

Experts caution against focusing solely on technology without considering long-term sustainability and creating innovative city solutions that adapt to future challenges and evolve as technology advances is essential.
Some of the challenges that experts identify include:
1. Data privacy and security

Data privacy and security are paramount, as using copious amounts of data can raise potential concerns.
2. Cost

Another paramount factor is the expense of these undertakings, as they can be somewhat expensive to implement and maintain.
3. Acceptance by citizens

Citizen acceptance is also vital, as the community must be open to these technologies’ changes.
4. Sustainability

Sustainability is a crucial factor to consider, as smart city technology must be environmentally friendly.
5. Governance

Establishing a clear governance framework is essential to ensure the success of innovative city projects.
Here are some specific expert opinions on smart cities:
1. Michael Batty, a distinguished urban planning professor at University College London, is recognized for his expertise in the field: “Smart cities are about using technology to make cities more efficient, livable, and sustainable. They can improve our lives in many ways, but some challenges must be addressed.”
2. Vinod Khosla co-founded Sun Microsystems: “Smart cities are the future of urban living. They will use technology to improve everything from transportation to energy and waste disposal. This will make cities more efficient, livable, and sustainable.”
3. Sebastian Thrun, former CEO of Google X: “Smart cities are the next big thing in urban planning. They will use technology to solve some of the biggest problems facing cities today, such as traffic congestion and pollution.”
| Read more: Top 10 Smart cities in the world |
E. What do Data and statistics represent about smart cities?
Understanding and evaluating the performance and impact of smart cities is crucial. Data and statistics are consequential in achieving this by providing priceless insights into different urban life factors and innovative city initiatives’ cogency. Some key areas where we can learn from data and statistics about smart cities:
1. Efficiency Metrics

Data can measure the efficiency of various urban systems, including transportation, energy consumption, and waste management. Statistics demonstrating reduced traffic congestion, shorter commute times, or lower energy consumption can highlight the advantages of smart city solutions.
2. Environmental Impact

Sustainability is a top priority for smart cities, and data and statistics can quantify the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, air quality improvements, and renewable energy sources. These metrics demonstrate the environmental impact of innovative city initiatives.
3. Resource Utilization

Data can track the use of water, electricity, and natural gas resources. Smart meters and sensors provide real-time data on consumption, improving resource management and conservation.
4. Public Safety

Statistics on crime rates, emergency service response times, and the effectiveness of surveillance systems can gauge the impact of innovative city technologies on public safety and security.
5. Economic Growth

Data can measure economic needles such as business growth, job creation, and investment in the city.
Innovative city initiatives that attract tech companies and startups can contribute to economic development.
6. Citizen Satisfaction

Surveys and data analysis can assess citizen satisfaction with city services and quality of life.
Feedback from residents can help city planners make improvements based on data-driven insights.
7. Traffic Management

Real-time traffic infusion from GPS devices, sensors, and cameras can optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve transportation efficiency.
8. Public Transportation

Data on ridership, punctuality, and user satisfaction can evaluate the effectiveness of intelligent public transportation systems.
It can also guide adjustments and improvements to transit services.
9. Digital Inclusion

Statistics on internet access, digital literacy, and technology adoption rates can indicate the city’s digital inclusion level, which is crucial for addressing the digital divide.
10. Infrastructure Health

Sensors and monitoring systems can collect data on infrastructure conditions like bridges, roads, and utilities.
This information helps prioritize maintenance and repairs.
11. Emergency Response

Data on response times, incident management, and disaster preparedness can assess the effectiveness of innovative city initiatives in handling emergencies.
12. Energy Efficiency

Data can track energy consumption patterns in buildings, public lighting, and other facilities.
Smart grids and energy management systems help optimize energy use and reduce costs.
13. Waste Management

Sensors in waste bins can provide data on waste collection needs, optimize routes, and reduce operational costs.
14. Education and Healthcare

Data can be used to estimate access to education and healthcare services, including enrollment rates, health outcomes, and utilization of telemedicine.
15. Tourism and Cultural Activities

Data on tourism trends, cultural events attendance, and visitor satisfaction can guide tourism and cultural promotion efforts.
F. What are the key features of smart cities?
A smart city is not defined universally, but it commonly includes the following key features:
Key features of a smart city:
1. Sustainability: Sustainability involves adopting renewable energy, enhancing energy efficiency, and reducing waste to minimize environmental impact.
2. Efficiency: Efficiency optimizes city operations, such as traffic, water, and waste management utilizing technology.
3. Livability: Livability sweetens residents’ grade of life by furnishing better healthcare, public transportation, and green spaces through technology.
4. Security: Technology enhances security with features like CCTV cameras, facial recognition software, and intelligent traffic lights.
5. Connectivity: Connectivity ensures high-speed internet access throughout the city, enabling efficient business operations and keeping citizens connected.
G. What are the most common technologies used in smart cities?
The prospect of intelligent cities to revolutionize our lifestyle and vocation civilization is immense, although the vision is still in its earlier stages. Using technology, elegant cities can increase sustainability, efficiency, and livability, promising a bright future for all.
A few commonly used technologies in smart cities include:
1. Internet of Things (IoT)

IoT involves physical objects with sensors, software, and network connectivity to collect and exchange data.
2. Big data

Big data collects massive and complex datasets that can reveal insights upon analysis.
3. Artificial intelligence (AI)
AI is the proficiency of machines to mimic human intelligence and is used for facial recognition, self-driving cars, and predictive analysis.
4. Blockchain

Blockchain provides a secure and transparent way to store data and is commonly used for tracking food deliveries, energy grid management, and identity verification in intelligent cities.
H. Top 10 Smart cities in the world
This list presents a limited view of the many philosophical cities worldwide. Thanks to specialized progress, we can expect to see even more creative and ambitious imaginative city projects. Below are ten of the most incredible intelligent cities worldwide, according to various sources:
10. Stockholm, Sweden

Stockholm, Sweden, is recognized for operating technology and data-driven explanations to sweeten sustainability, urban life, and efficiency. Stockholm’s innovative city features are as follows:
i. Advanced Public Transportation: Stockholm has an exceptionally efficient public transportation system with integrated ticketing and real-time updates for buses, trams, subways, and ferries. Elegant traffic management systems have been executed to miscalculate congestion and enhance traffic flow.
ii. Environmental Sustainability: Stockholm is dedicated to sustainability, with initiatives such as “Vision Zero” for traffic safety and extensive green spaces. The city promotes cycling and electric vehicle adoption through infrastructure and incentives.
iii. Digital Services: Residents can access digital services, including online permits, e-government platforms, and mobile apps that provide city information and services.
iv. Smart Buildings and Infrastructure: Stockholm encourages intelligent building practices, such as energy-efficient construction and IoT-based building management systems. District heating and cooling systems contribute to energy efficiency.
v. Waste Management: Smart bins and waste collection systems optimize garbage collection routes, reducing costs and environmental impact. Recycling and waste reduction programs are also actively promoted.
vi. Education and Innovation: Stockholm fosters innovation by cooperating with research institutions, universities, and tech companies. It has a thriving startup ecosystem and hosts events like Stockholm Tech Fest to showcase innovation.
vii. Digital Healthcare: Stockholm operates electronic medical records, e-health solutions, and telemedicine to sweeten healthcare access and efficiency. Patients can access medical records and book appointments online.
viii. Green Spaces and Parks: The city strongly emphasizes green urban planning, ensuring that parks and recreational areas are easily accessible to residents.
ix. Smart Lighting and Energy Management: The city employs intelligent lighting systems that adjust based on natural light and occupancy, reducing energy consumption. Public buildings and streetlights are equipped with energy-efficient technologies.
x. Water Management: Stockholm manages its water resources efficiently with intelligent systems for monitoring water quality and consumption. The city is proactive in mitigating water-related challenges.
xi. Data Privacy and Security: Stockholm prioritizes data security and privacy to protect residents’ and businesses’ personal information.
xii. Cultural and Social Initiatives: The city uses technology to elevate cultural events and social engagement, sweetening the grade of life for its residents.
xiii. International Collaboration: Stockholm collaborates with other smart cities and participates in global networks to exchange best practices and stay at the forefront of innovative city development.
xiv. Public Safety and Security: Intelligent surveillance and emergency response systems enhance public safety. Stockholm utilizes technology to respond quickly to emergencies and natural disasters.
xv. Inclusive Urban Planning: Stockholm emphasizes inclusive urban planning, ensuring that innovative city initiatives benefit all residents, including those with disabilities and elderly citizens.
In summary, Stockholm has operated technology and sustainability ambitions to transform into an intelligent city, sweetening the life grade for its inhabitants while focusing on environmental conservation and efficiency.
9. Zurich, Switzerland

Zurich, Switzerland, has assembled a great stride in becoming a smart city. Some of the key achievements:
i. Efficient Public Transportation: Zurich has an effective public transportation system, including punctual trams, buses, and trains. Smart ticketing is also utilized to make travel simpler and more efficient.
ii. Sustainable Urban Planning: Zurich prioritizes sustainability in its urban planning, focusing on green spaces, energy-efficient buildings, and reducing emissions.
iii. Clean Energy: Zurich is committed to clean energy production and consumption, promoting clean energy sources.
iv. Digital Governance: Zurich uses digital tools for citizen engagement, e-government services, and data-driven policy-making.
v. Waste Management: Zurich has optimized waste collection through smart bins and recycling programs, creating a cleaner environment.
vi. Education and Innovation: Research and innovation are supported through partnerships with universities and tech industries.
vii. Digital Healthcare: Digital healthcare solutions are implemented in Zurich to improve patient care and streamline healthcare administration.
viii. Smart Lighting: Energy-efficient intelligent lighting systems are utilized in public areas to save energy.
ix. Water Management: Technology efficiently manages water resources while ensuring a sustainable supply.
x. Data Privacy and Security: Data protection and cybersecurity are prioritized in Zurich to safeguard residents’ information.
xi. Public Safety: Smart surveillance and emergency response systems enhance public safety and security.
xii. Cultural and Social Initiatives: Zurich utilizes technology to promote cultural events and social engagement, improving residents’ quality of life.
xiii. International Collaboration: Zurich collaborates with other smart cities to share best practices and stay at the forefront of innovative city development.
These achievements demonstrate how Zurich leverages technology and sustainability practices to improve urban living and efficiency, making it a smart city.
8. Helsinki, Finland

7. Oslo, Norway

6. Barcelona, Spain

5. New York City, USA

New York City has implemented an intelligent city approach to sweeten urban living, efficiency, and sustainability. Its smart city infrastructure comprises various features, including:
i. Public Transportation: NYC has a vast subway system and buses supported by real-time tracking and contactless payment options.
ii. Digital Services: The city offers online government services such as permits and information access, simplifying interactions with the government.
iii. Environmental Sustainability: NYC promotes sustainability through initiatives like green building practices, bike lanes, and programs to reduce emissions.
iv. Smart Infrastructure: The city invests in intelligent infrastructure, such as LED streetlights, utilities based on the Internet of Things, and waste management systems.
v. Innovation Hubs: New York City has many startups, tech hubs, and research institutions that promote invention and entrepreneurship.
vi. Data Analytics: The city uses data analytics for urban planning, traffic management, and crime prevention, improving overall efficiency.
vii. Cultural and Social Initiatives: Technology enhances cultural events, public art installations, and social engagement, enriching the lives of residents.
viii. Digital Healthcare: NYC utilizes digital health resolutions to sweeten patient care, telemedicine, and electronic health records.
ix. Data Privacy and Security: Strong data protection measures are in place to safeguard residents’ personal information.
x. Public Safety: Smart surveillance systems and emergency response technologies enhance public safety and security.
xi. Waste Management: NYC optimizes waste collection with smart bins, recycling initiatives, and waste-to-energy facilities.
xii. International Collaboration: The city cooperates with other towns and elegant experiences in global networks to convey best practices and stay at the forefront of innovative city development.
These points illustrate how New York City influences technology and sustainability measures to sweeten the grade of life for its inhabitants while facilitating environmental conservation and innovation.
4. Copenhagen, Denmark

Copenhagen, Denmark, is a renowned smart city that has successfully implemented numerous sustainable initiatives and technologies. The following are some of the city’s notable features:
i. Biking Culture: Copenhagen is famous for its biking culture, which encourages eco-friendly transportation and decreases traffic congestion.
ii. Renewable Energy: The city invests in renewable energy, including wind and solar power, district heating, and energy-efficient buildings, to become carbon-neutral by 2025.
iii. Smart Transportation: Copenhagen offers efficient public transportation, like a metro system, promotes electric buses, and has an extensive charging station network.
iv. Digital Services: Residents benefit from online permits, digital government services, and simple-to-use platforms for accessing city information through digital services.
v. Sustainable Urban Planning: Copenhagen prioritizes green spaces, pedestrian zones, and eco-friendly architecture in urban development as part of its sustainable urban planning.
vi. Innovation Districts: Copenhagen has districts that foster innovation, such as Copenhagen Science City and the Danish Technological Institute.
vii. Waterfront Development: The city uses intelligent urban planning to revitalize waterfront areas, creating recreational and cultural spaces.
viii. Waste Management: Copenhagen optimizes waste collection with smart bins, recycling programs, and waste-to-energy facilities.
ix. Data Privacy and Security: The city has robust data protection measures to safeguard citizens’ personal information.
x. Public Safety: Smart surveillance systems and emergency response technologies enhance public safety.
xi. Cultural and Social Initiatives: Technology promotes cultural events, social engagement, and public art installations, enriching residents’ lives.
xii. International Collaboration: Copenhagen cooperates with other intelligent cities and experiences in global networks to intercommunication best conventions and advances innovative city development.
These points exemplify how Copenhagen connects technology and sustainability procedures to create an intelligent city that prioritizes the well-being of its citizens, environmental stewardship, and innovation.
3. Amsterdam, Netherlands

London, UK, has executed several innovative city endeavors to enrich urban living, promote sustainability, and increase efficiency. Several key features are highlighted below:
i. Transportation: London has an extensive public transportation system with contactless payment options and real-time tracking for buses and trains.
ii. Environmental Sustainability: The city announces sustainability through varied enterprises, such as congestion cycling infrastructure, pricing, and emissions reduction programs.
iii. Digital Services: London provides convenient online government services and mobile apps for residents to access city information and services.
iv. Smart Infrastructure: London invests in intelligent infrastructure, including energy-efficient buildings, IoT-based utilities, and waste management systems.
v. Cultural and Social Initiatives: Technology is used to promote cultural events, social engagement, and public art installations, enriching the lives of its residents.
vi. Innovation Ecosystem: London supports innovation and startups through tech hubs, accelerators, and initiatives that foster entrepreneurship.
vii. Digital Healthcare: E-health solutions and electronic medical records are leveraged to improve healthcare access and quality.
viii. Data Privacy and Security: The city strongly emphasizes data security and privacy to protect residents’ personal information.
ix. Public Safety: Smart surveillance systems and emergency response technologies enhance public safety and security.
x. Waste Management: London optimizes waste collection with smart bins and recycling programs, reducing environmental impact.
xi. Green Spaces: Extensive green spaces and parks are maintained throughout the city, balancing urban life and nature.
xii. International Collaboration: London cooperates with other intelligent cities and global networks to disseminate best practices and dwell at the forefront of innovative city development.
These initiatives exemplify London’s commitment to incorporating technology and sustainability measures to benefit residents and the environment.
1. Singapore

Singapore is globally acknowledged as an intelligent city that operates technology and data-driven resolutions to sweeten its inhabitants’ quality of life and operational efficiency. Some key areas that emphasize Singapore’s transformation into a smart city:
i. Digital Infrastructure: The city-state has invested considerably in creating a robust digital infrastructure, encompassing high-speed internet access and widespread connectivity. This forms a solid foundation for various intelligent initiatives.
ii. Smart Transportation: Singapore’s well-integrated public transportation system offers real-time tracking and payment options, encourages the use of electric vehicles, and has established EV charging infrastructure.
iii. Urban Planning and Design: Singapore employs data and simulations for urban planning to optimize land use and infrastructure development. The city prioritizes green spaces and sustainable design principles.
iv. Smart Governance: The government leverages data analytics and AI to assemble educated policy decisions and sweeten public services. The “Smart Nation” program underscores citizen hire and digital government services.
v. Efficient Healthcare: Singapore utilizes electronic health records, telemedicine, and wearables to enhance healthcare services. The HealthHub initiative empowers citizens with health information.
vi. Education Technology: Singapore’s education sector employs technology for remote learning, personalized education, and teacher training. The government supports initiatives to develop a skilled workforce in emerging tech fields.
vii. Smart Energy Management: The city promotes energy efficiency and has implemented smart grids to monitor and manage electricity consumption. It also encourages the use of solar panels and green building practices.
viii. Waste Management: Singapore optimizes waste collection through sensors and data analytics, reducing costs and environmental impact. The city has recycling and sustainability programs in place.
ix. Safety and Security: Singapore uses philosophical surveillance systems and analytics to enrich public safety. Emergency kindnesses have access to real-time data and technology for quick comeback.
x. Smart Water Management: Singapore employs technology to ensure a sustainable water supply. Sensors monitor water quality and consumption.
xi. Tourism and Hospitality: Singapore’s tourism industry incorporates intelligent technologies, offering tourists convenient services like virtual tours and mobile apps.
xii. Innovation Ecosystem: Singapore has created a passionate ecosystem for startups and creation, attracting tech talent and investment. It hosts events like the Singapore FinTech Festival to facilitate innovation in finance and beyond.
xiii. Sustainability Initiatives: Singapore promotes sustainable practices like vertical farming and green building standards. Initiatives like the “Zero Waste Masterplan” aim to reduce waste and encourage recycling.
xiv. Data Privacy and Security: Singapore strongly emphasizes data protection and cybersecurity to ensure the safety and privacy of its citizens’ data.
xv. International Collaboration: Singapore cooperates with other elegant cities and international organizations to intercommunication the most pleasing practices and stay at the vanguard of innovative city development.
These points affirm Singapore’s adoption of technology and data-driven resolutions to transform into a brilliant city, improving the well-being of its tenants and the overall efficiency of its procedures.


