Table of Contents
1. What is a Plate Load Test?
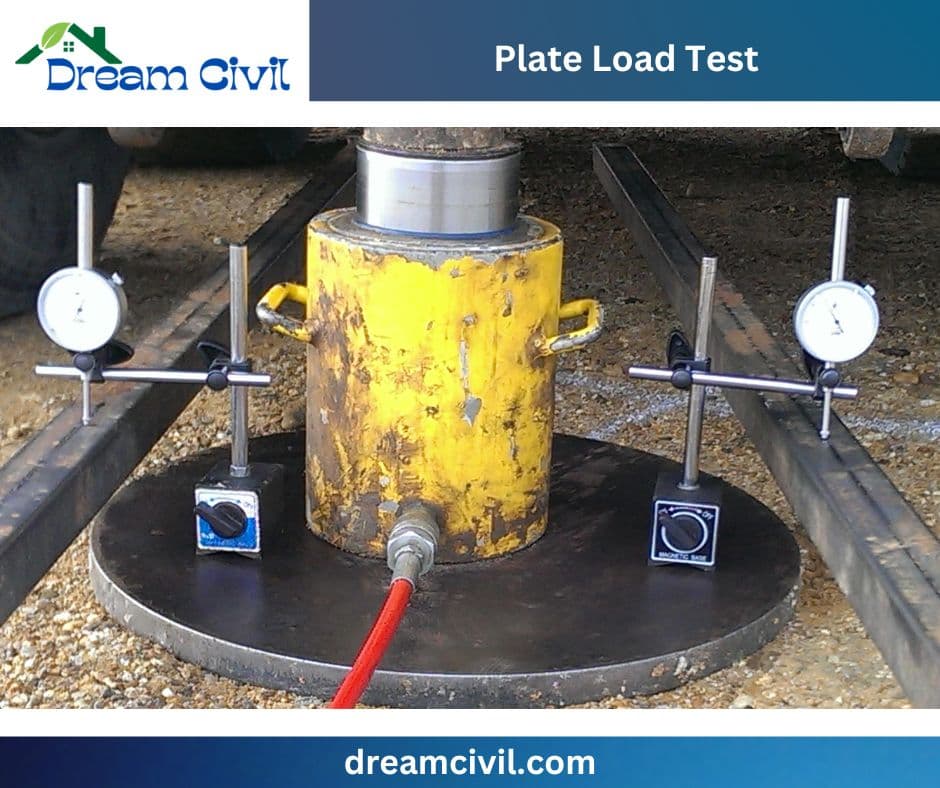
✔ A Plate Load Test is a technique typically utilized in civil and geotechnical engineering to consider the subsurface’s bearing power and settlement features.

✔ This test entails recognizing a rigid steel plate (usually circular or square) on the ground, laying a controlled load on it, and then calculating the resulting deformation or compromise.
✔ This method helps engineers and geotechnical experts assemble essential data for creating structures such as foundations, pavements, and other constructions by specifying how the soil bears under load.
✔ The Plate Load Test is efficient and beneficial to assure the safety and strength of construction projects by examining the soil’s capability to resist set loads.
2. How is a Plate Load Test Conducted?

✔ The Plate Load Test is an exhaustive approach carried out in several steps to estimate the load-bearing capability and settlement attributes of the soil under the test location. Let me know via the widespread outline of how the test is conducted:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Site | ✔ Select and prepare the test location. |
| Equipment Setup | ✔ Place plate and install displacement devices. |
| Application of Load | ✔ Apply known, controlled load to the plate in increments. |
| Data Collection | ✔ Record the applied load and corresponding settlements at each load increment. |
| Unloading and Recovery | ✔ Unload the plate and monitor the recovery of soil deformation. |
| Test Completion | ✔ Gather data and measurements for analysis. |
| Reporting and Analysis | ✔ Provide a detailed report of test results. |
✔ Conducting the Plate Load Test in harmony with designated criteria and guidelines is essential to guarantee the soil behavior review’s accuracy and reliability. It is compulsory to note that the precise testing strategy may vary depending on the project needs and the standards followed by the testing association or advisor.
3. What are the Benefits of a Plate Load Test?
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Foundation Design | ✔ Ensure safe support for structures. |
| Soil Properties | ✔ Understand bearing capacity and settlement. |
| Site-Specific Data | ✔ Tailor designs to unique conditions. |
| Stability Assessment | ✔ Crucial for safety and durability. |
| Quality Control | ✔ Verify construction materials and methods. |
| Preventing Failures | ✔ Avoid construction issues and settlement. |
| Cost Efficiency | ✔ Lead to cost-effective designs and methods. |
| Structural Integrity | ✔ Contribute to structural strength. |
| Safety Assurance | ✔ Enhance safety and reduce risks. |
| Data-Driven Decisions | ✔ Make informed choices during projects. |
4. When is a Plate Load Test Required?
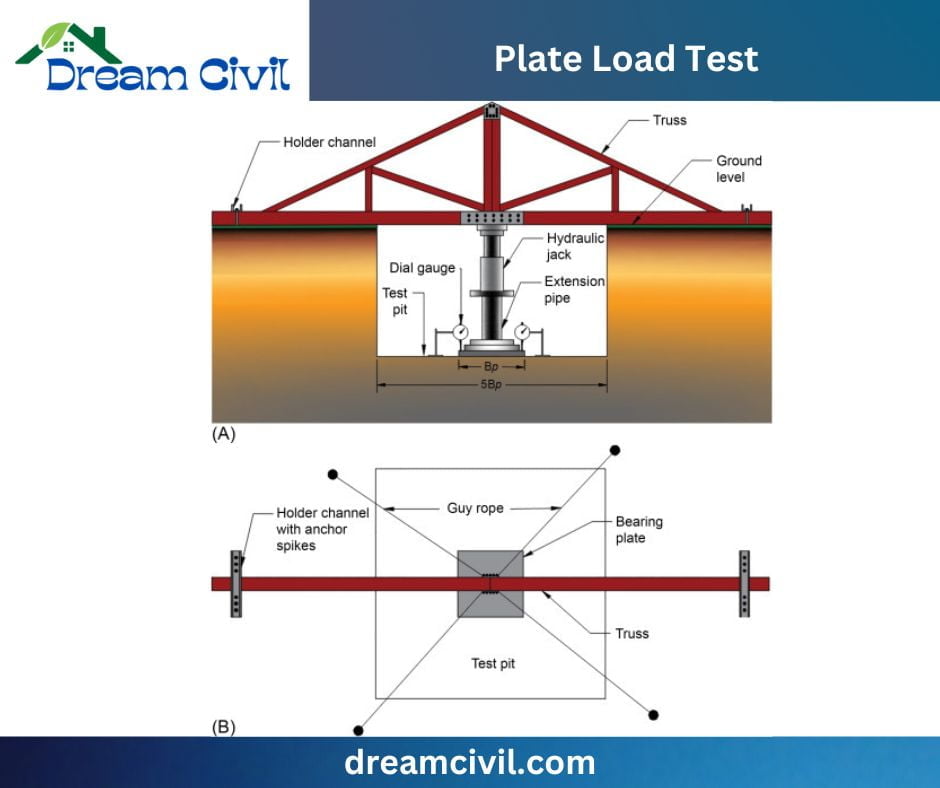
I. Foundation Design: Plate Load Tests are essential for engineers to specify whether the soil can safely sustain the planned load for buildings, bridges, or pavements.
II. New Construction: By conducting these tests, engineers can make instructed conclusions about foundation design and construction techniques before beginning construction projects, specifically those involving heavy loads.
III. Remediation and Rehabilitation: Plate Load Tests can also be utilized to estimate the soil’s ability to handle extra loads or to determine the reasons for problems like settlement, which is incredibly important when there are worries about the stability of existing structures or foundations.
IV. Quality Control: Contractors can conduct PLTs during construction to verify that construction textiles and methodologies complete design specifications, delivering the grade and safety of the concluded structure.
V. Site-Specific Needs, Safety, and Compliance: In some regions, local building codes or regulations may require Plate Load Tests for essential facilities or projects in seismically operational areas to provide structures’ safety and structural integrity.
VI. Geotechnical Investigations: Geotechnical investigations also use Plate Load Tests to assess soil properties, authorizing construction and foundation design guidance when trading with unique or challenging site conditions like the soil with unknown parcels or non-standard construction necessities.
Overall, Plate Load Tests are a beneficial tool for evaluating soil suitability, providing the safety and quality of construction projects, and delivering recommendations for foundation design.
5. What is the difference between plate load and static cone penetration tests (SCPT)?
| Characteristic | Plate load test | SCPT |
|---|---|---|
| Test type | ✔ In-situ loading test | ✔ In-situ penetration test |
| Test method | ✔ Applies a load to a steel plate and measures settlement | ✔ Pushes a cone-shaped penetrometer into the ground and measures resistance to penetration |
| Test depth | ✔ Typically shallow (less than 1 meter) | ✔ Typically deep (several meters) |
| Typical applications | ✔ Foundation design, settlement evaluation | ✔ Foundation design, pavement design, slope stability assessment, ground improvement |
| Objective | ✔ Assess soil-bearing capacity and deformation under a specific load | ✔ Characterize subsurface soil profile and understand soil properties |
| Loading method | ✔ Apply controlled load directly to the ground surface | ✔ Measure cone resistance and frictional forces as the cone penetrates soil |
| Applications | ✔ Structural and foundation design | ✔ Geotechnical investigations and soil characterization |
| Data output | ✔ Bearing capacity and settlement | ✔ shear strength, relative density, Soil stratigraphy, and other soil properties |
6. How to Interpret the Results of a Plate Load Test?

| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Load-Settlement Curve | ✔ Plot load-settlement curve using data from the PLT. |
| Ultimate Bearing Capacity | ✔ Determine the point on the curve where the settlement rate increases significantly. |
| Safe Bearing Capacity | ✔ Divide ultimate bearing capacity by a safety factor to obtain safe bearing capacity. |
| Allowable Settlement | ✔ Assess whether an observed settlement is within acceptable limits. |
| Soil Type and Behavior | ✔ Analyze soil type and behavior based on the curve’s characteristics. |
| Load-Distribution Factors | ✔ Examine the uniformity of settlement across the plate. |
| Time-Dependent Behavior | ✔ PLTs can deliver insights into the soil’s time-dependent behavior. |
| Soil Modulus | ✔ Calculate the soil modulus, which quantifies the stiffness of the soil. |
| Consultation with Geotechnical Engineers | ✔ Geotechnical engineers should review and analyze PLT results. |
| Correlation with Other Test Data | ✔ Cross-reference PLT results with other geotechnical data. |
| Design Implications | ✔ Make design decisions regarding the foundation type, size, and depth. |
| Documentation and Reporting | ✔ Prepare a detailed report that includes all relevant data. |
7. Plate Load Tests for Residential Foundations
1. When required: heavy loads, slopes, Soft soil, flood/quake-prone areas.
2. Procedure: Geotechnical engineers pack a steel plate on the ground surface and estimate settlement. The test is recounted at growing loads until a specific settlement brinks or the soil’s load power is reached.
3. Analysis: The test effects specify the soil’s bearing power and the foundation’s settlement features.
4. Benefits: Delivers precise and accurate measurements of soil bearing capacity, settlement features, and benefits to identify weak soil layers.
5. Conclusion: Plate load tests are a worthwhile tool for creating safe and cost-effective residential foundations, but they are not typically required.
8. Plate Load Tests for Commercial Foundations
1. Purpose: Estimate soil-bearing ability and deliver valuable data for foundation design and construction, contributing to the stability and safety of retail foundations.
2. Procedure:
✔ Pick a test zone that accurately describes soil conditions across the project area.
✔ Organize the test area by clearing debris, vegetation, and obstructions.
✔ Set a rigid, known-area plate on the organized surface and lodge displacement transducers around the perimeter to monitor settlement.
✔ Lay the load incrementally and monitor the plate for settlement.
3. Analysis:
✔ Select the ultimate bearing ability from the point on the load-settlement curve where the recompense rate substantially increases.
✔ Lay a safety factor to pick a safe bearing capacity.
✔ Estimate acceptable settlement to ensure it does not compromise the structure’s stability or functionality.
✔ Examine soil properties and manners based on the load-settlement curve.
4. Design:
✔ Use the cracked PLT results to design the commercial foundation regarding foundation type, depth, size, and underpinning requirements.
5. Documentation:
✔ Schedule a comprehensive report including the load-settlement curve, most excellent bearing capacity, safe bearing capacity, soil modulus, and other relevant data.
6. Benefits of PLTs for commercial foundations:
✔ Commercial foundations are developed to withstand expected loads while controlling settlement-related issues.
✔ Qualify for the secure and practical design of foundations for retail structures such as office buildings, warehouses, and retail facilities.
7. Conclusion:
✔ Plate load tests are essential for evaluating soil-bearing ability and designing safe and dependable foundations for saleable buildings and structures.
9. Plate Load Tests for Industrial Foundations
1. Purpose: Set soil-bearing power and deformation features to create safe and economical foundations for extensive, weighty industrial structures.
2. Procedure:
✔ Pick a test site that nearly reaches the foundation site.
✔ Lay the load on a steel plate on the ground surface and estimate settlement.
✔ Repeat the test at boosting loads until the plate reaches a certain settlement threshold or the soil’s load power.
3. Analysis:
✔ Specify the soil’s bearing capacity and the foundation’s territory characteristics.
4. Benefits:
✔ Deliver accurate and direct sizes of the soil’s bearing capacity.
✔ Consider the soil’s settlement features.
✔ Pinpoint weak soil layers and develop appropriate foundations.
✔ Confirm the design hypotheses used in the foundation’s design.
5. Conclusion:
✔ Plate load tests are beneficial for designing safe and economical foundations for industrial structures. They are quick, easy to operate, and can be performed on diverse soil types.
10. Plate Load Tests for Roadways and Bridges
Purpose: Set soil-bearing capacity and settlement features to make safe and stable pavements and bridges.
Procedure:
✔ Pick a test location that accurately describes the soil conditions at the site.
✔ Lay the load on a steel plate on the bottom surface and estimate settlement.
✔ Repeat the test at raising loads until the plate gets a certain settlement threshold or the load power of the soil is acquired.
Analysis:
✔ Pick the soil’s bearing ability and the settlement features of the roadway or bridge.
Benefits:
✔ Furnish precise dimensions of the soil’s bearing capacity.
✔ Consider the soil’s settlement features.
✔ Pinpoint weak soil layers and create appropriate pavements or bridges.
Conclusion:
✔ Plate load tests are a practical and beneficial tool for designing safe and economical pavements and bridges. They are moderately quick and easy to conduct and can be performed on various soil types, making them a worthwhile and cost-effective solution for considering soil conditions.

